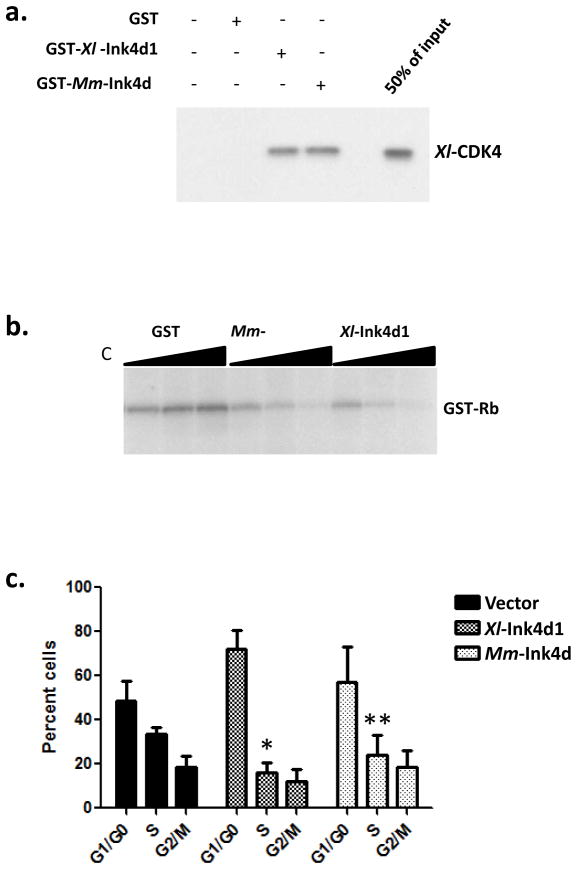
Figure 3.
Xl-Ink4d is a cyclin D-dependent Cdk4 inhibitor. (a) The indicated GST fusion proteins were expressed in bacteria and purified on glutathione sepharose. The adsorbed sepharose was incubated with in vitro transcribed and translated [35S]-labeled Xenopus Cdk4 (Xl-Cdk4), washed and separated on an SDS-polyacrylamide gel. 50% of the input Xl-Cdk4 that was used for pull-downs was run to estimate the percent of starting material that bound to the GST fusion protein (50% input). (b) Cdk4 kinase reactions were run with increasing amounts of purified GST-Xl-Ink4d1 and GST-Mm-Ink4d (mouse Ink4d) fusion proteins. Active mouse Cdk4/cyclinD1 kinase complexes were generated from SF9 cells infected with baculoviruses encoding mouse Cdk4 and cyclin-D1. Kinase assays were performed with [γ-32P]-ATP using purified GST-Rb as substrate. (c) The cell cycle profile of NIH-3T3 mouse fibroblasts overexpressing vector-alone (black bars), Xenopus Xl-Ink4d1 (dark grey bars) or mouse Mm-Ink4d (light grey bars). NIH-3T3 cells were infected with retroviruses that co-express the indicated Ink4d genes and GFP, and the DNA content of GFP-positive cells was measured by propidium iodide staining and FACS analysis. The percentage of cells in G1/G0, S and G2/M phase is presented. Expression of either Xl-Ink4d1 (* p=0.006) or Mm-Ink4d (** p=0.05) shows a significant decrease in S phase compared to vector alone.