Figure 4. SUMO1 prevents glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor-dependent inhibition of α-cell Na+ currents.
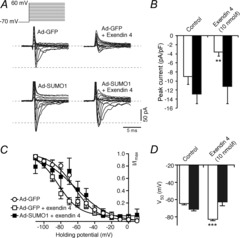
We measured voltage-dependent Na+ currents in mouse α-cells, positively identified by glucagon immunostaining, in the whole-cell configuration. A, representative responses to a series of membrane depolarizations from a holding potential of −70 mV in α-cells infected with green fluorescent protein (Ad-GFP) and exposed to 0 nm or 10 nm exendin 4 during the experiment, and in α-cells infected with SUMO1 (Ad-SUMO1) then treated with 0 nm or 10 nm exendin 4. B, quantification of peak Na+ currents in cells infected with Ad-GFP (open bars) or Ad-SUMO1 (black bars). C, exendin 4 (10 nm) inhibits α-cell Na+ currents by causing a leftward shift of voltage-dependent inactivation (open squares). This is prevented by upregulation of SUMO1 (black squares). D, half-maximal current inactivation (V50) is shown for cells infected with Ad-GFP (open bars) or Ad-SUMO1 (black bars). *P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 for comparisons with the control.
