Figure 2.
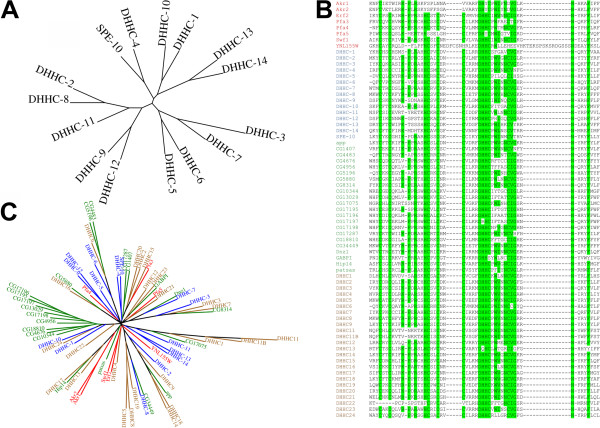
Phylogenetic analysis of DHHC enzymes from yeast, worms, fruit flies and humans. (A) The 15 DHHCs from C. elegans were subjected to phylogenetic analysis and the resulting trees were rendered using Interactive Tree of Life [71]. (B) An alignment of the DHHC-motif cysteine-rich domain (DHHC-CRD) of the known DHHC enzymes from S. cerevisiae (red lettering), C. elegans (blue), D. melanogaster (green) and H. sapiens (brown) is shown. Specific residues in the consensus sequence Cx2Cx3(R/K)PxRx2HCx2Cx2Cx4DHHCxW(V/I)xNC(I/V)Gx2Nx3F [1] are highlighted in light green. (C) The conserved DHHC-CRD from these organisms (C) was also subjected to phylogenetic analysis. Species and colours are as in panel (B).
