Figure 2. Lineage of Dlx5-expressing cells in the maxillary arch.
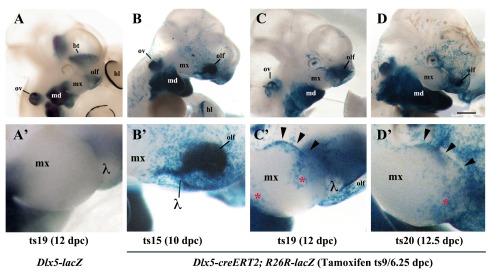
ß-Galactosidase activity in the cephalic region of Dlx5-lacZ ( A, A’) and Dlx5-creERT2; R26R-lacZ mouse embryos ( B– D’). In all cases pregnant dams were treated with tamoxifen at 6.25 dpc/Theiler stage 9 (ts9) and embryos were collected at the indicated Theiler stage. ( A, A’) As expected, even after tamoxifen treatment, Dlx5 is expressed in the mandibular arch (md), in the olfactory pit (olf), in the otic vesicle (ov), in the basal telencephalon (bt) and in the hind limb (hl), but not in the maxillary arch. ( B, B’) Permanent activation of lacZ reporter expression in derivatives of Dlx5-expressing early progenitors (ts9) reveals the presence of a positive cellular contingent in the ts15 lambdoidal junction (λ) between the olfactory pit and the maxillary process. ( C, C’; D, D’) At later developmental stages (ts19, ts20) a contingent of lacZ positive cells populates the distal domain of the maxillary arch. hl, hind limb; md, mandibular arch; mx, maxillary arch; olf, olfactory pit; ov, otic vesicle; bt, basal telencephalon; λ, lambdoidal junction; red asterisk/black arrowheads, territories of the maxillary arch colonized by derivatives of Dlx5-expressing progenitors. Bar: A– D 1mm; A’– D’ 250µm.
