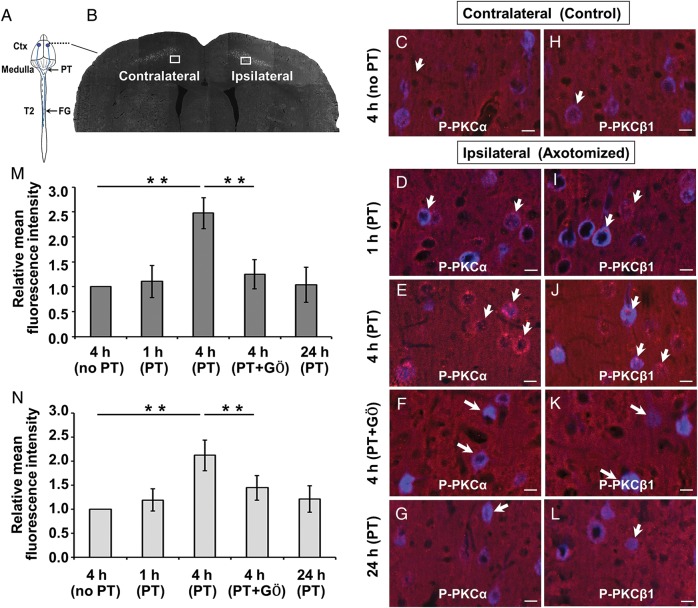
Figure 2.
Cortical delivery of GÖ6976 effectively blocks the activation of PKCα and PKCβ1 in corticospinal neurons following pyramidotomy. (A) Schematic drawing of the experimental design showing the sites of FG injection, pyramidotomy, and observation (Ctx). (B) A coronal section shows FG retrogradely labeled CST neurons on both the contralateral (control) and ipsilateral (axotomy) sides to the pyramidotomy. Boxed areas indicate where p-PKCα (C–G) and p-PKCβ1 (H–L) immunoreactivity (IR) were examined. Compared with the contralateral CST motoneurons (C and H), p-PKCα and p-PKCβ1 IR (red, short arrows) increased at 1 h (D and I), peaked at 4 h (E and J), and returned to the normal level at 24 h (G and L) in the FG-labeled corticospinal neuronal soma (blue, long arrows) after ipsilateral pyramidotomy. Cortical delivery of GÖ6976 significantly blocked the expression of p-PKCα and p-PKCβ1 in CST motoneurons (F and K, arrows). (M and N) Quantification of the relative mean fluorescence intensity of p-PKCα (M) and p-PKCβ1 (N) at different time points between different groups. (**P < 0.01). Scale bars = 15 µm.