Figure 3.
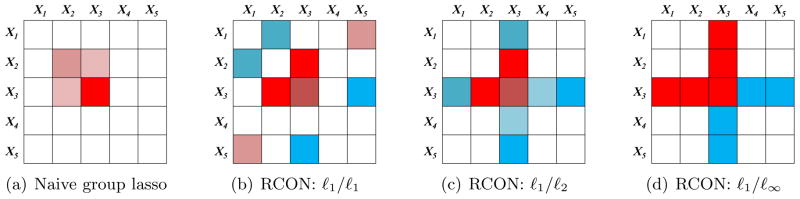
Toy example of the results from applying various penalties in order to estimate a 5×5 matrix, under a symmetry constraint. Zero elements are shown in white; nonzero elements are shown in shades of red (positive elements) and blue (negative elements). (a): The naive group lasso applied to the columns of the matrix yields non-zero elements that are the intersection, rather than the union, of a set of rows and columns. (b): The RCON penalty using an ℓ1/ℓ1 norm results in unstructured sparsity in the estimated matrix. (c): The RCON penalty using an ℓ1 / ℓ2 norm results in entire rows and columns of non-zero elements. (d): The RCON penalty using an ℓ1/ℓ∞ norm results in entire rows and columns of non-zero elements; many take on a single maximal (absolute) value.
