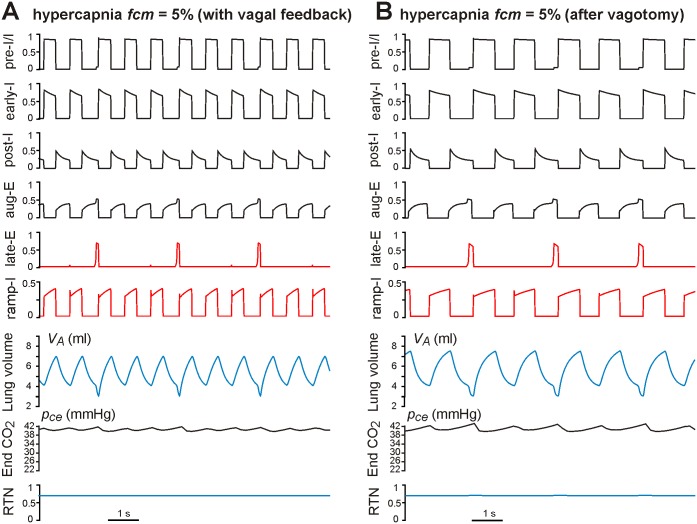
Figure 4. Effects of hypercapnia maintained at fcm = 5% in the intact (A) and vagotomized (B) models.
fcm is CO2 content in the mouth. In both cases, hypercapnia evoked increases in RTN drive (bottom traces in A and B). The applied hypercapnia increased the RTN drive to the late-E neuron evoking late-E discharges with the ratio 1∶3 to the ramp-I discharges in the vagus intact model (late-E trace in A) and the ratio 1∶2 in the vagotomized model (late-E trace in B). Each late-E pulse actuates the abdominal pump, reducing the base level of lung volume (see VA traces in A and B).