Figure 1. Schematic of the fibre-laser system and SRS microscope.
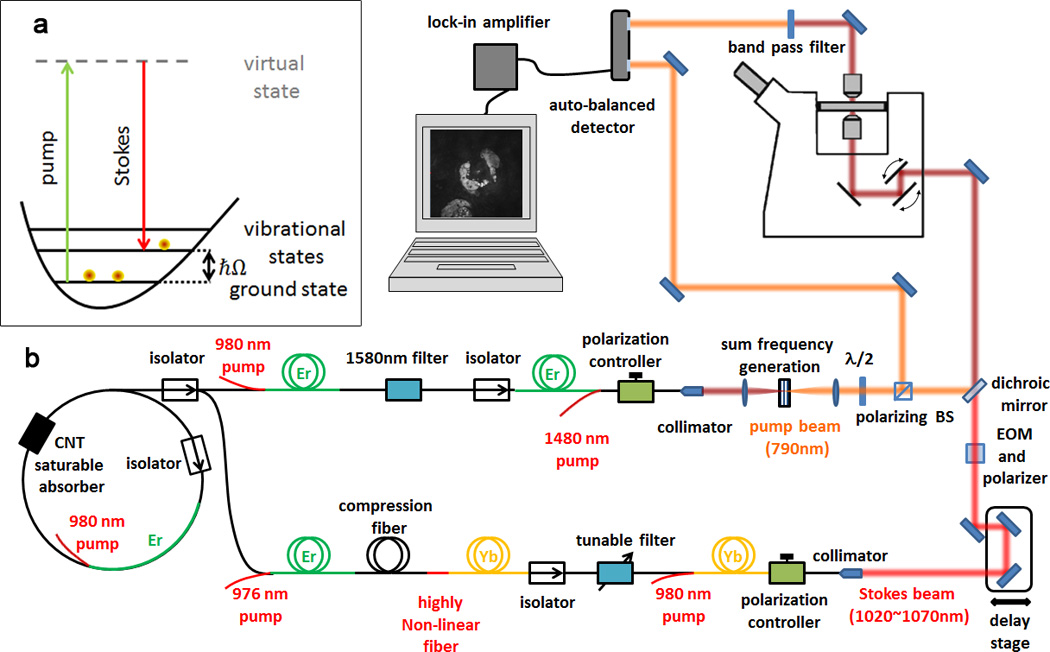
a, Energy diagram of SRS. When the difference in photon energy between the pump and the Stokes beam matches the energy of a vibrational state of the target molecule, ħΩ, molecules are efficiently excited from the ground to the corresponding excited state and a pump photon is absorbed (stimulated Raman loss, SRL) and a Stokes photon is generated (stimulated Raman gain, SRG). b, Schematic of the fibre laser. The laser system starts with an Er-doped fibre oscillator, which is mode-locked with a carbon nanotube (CNT) saturable absorber. The output is split into two arms to generate the pump (upper arm) and Stokes (lower arm) beams. The Stokes beam is modulated at 10MHz with an electro optic modulator (EOM), temporally and spatially combined with the pump beam, and aligned into to a beam-scanning microscope. The transmitted beams are collected with a condenser. The pump beam is detected by the autobalanced detector after the Stokes beam is blocked with an optical filter. The reference beam is sampled in front of the microscope with a polarizing beam splitter (BS).
