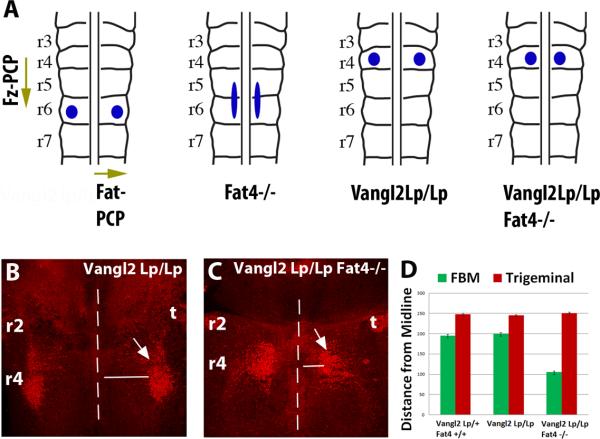
Figure 4. Fat-PCP and Fz-PCP act along orthogonal axes to guide FBM neuronal migration.
(A) Schematics showing Fz-PCP and Fat-PCP regulation of FBM neuronal tangential migration along orthogonal axes. The blue circles/ellipse indicate the final position of the FBM at E14.5 in wildtype, Fat4−/− (and Dchs1−/−), Vangl2LpLp and Vangl2LpLp Fat4−/− mouse mutants. (B-D) FBM neuronal migration visualised by Islet1 immunostaining (red, arrowed) in Vangl2LpLp and Fat4−/−/Vangl2 LpLp E13.5 embryos. The FBM neurons have been viewed from the pial surface. The midline is indicated by a dashed line. The extent of lateral migration of the FBM, and the control trigeminal neuron which is unaffected, is quantified in (D). r, rhombomere; t, trigeminal