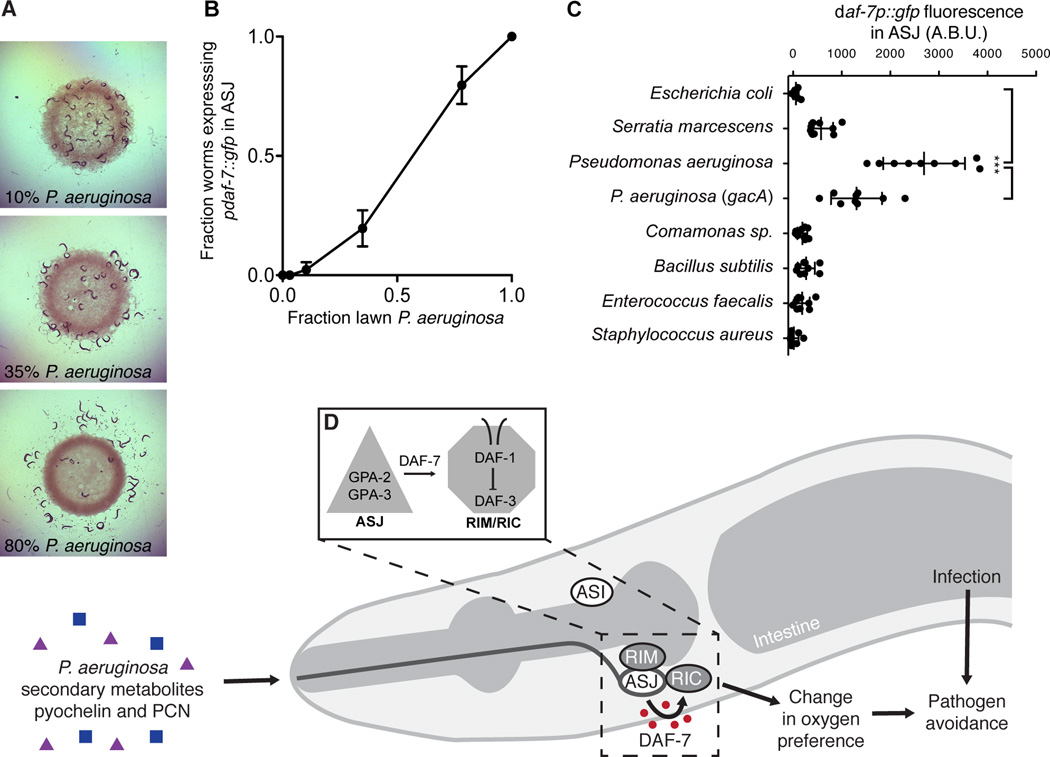
Figure 7. Microbial discrimination of P. aeruginosa activates daf-7 transcription in the ASJ neurons and promotes avoidance behavior.
(A) C. elegans after 16 h exposure to bacterial lawns consisting of E. coli OP50 and P. aeruginosa PA14. Fraction of bacteria that were P. aeruginosa when daf-7p∷gfp was assayed is indicated. (B) Fraction of animals expressing daf-7p∷gfp in the ASJ neurons after 16 h exposure to E. coli, P. aeruginosa, or mixtures of E. coli and P. aeruginosa. Error bars indicate standard deviation. (C) Maximum fluorescence values of daf-7p∷gfp in ASJ neurons after 16 h exposure to indicated bacteria. *** P < 0.001 as determined by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s Multiple Comparison Test. Error bars indicate standard deviation. (D) In response to P. aeruginosa exposure, or P. aeruginosa metabolites phenazine-1-carboxamide (PCN) and pyochelin, daf-7 expression is activated via G-protein alpha subunits GPA-3 and GPA-2 in the ASJ neurons. Secreted DAF-7 signals to the TGF-β receptor DAF-1 the adjacent RIM/RIC interneurons. DAF-7/TGF-β signaling acts to alter aerotaxis behavior and promote avoidance of pathogenic bacteria.