Fig. 1.
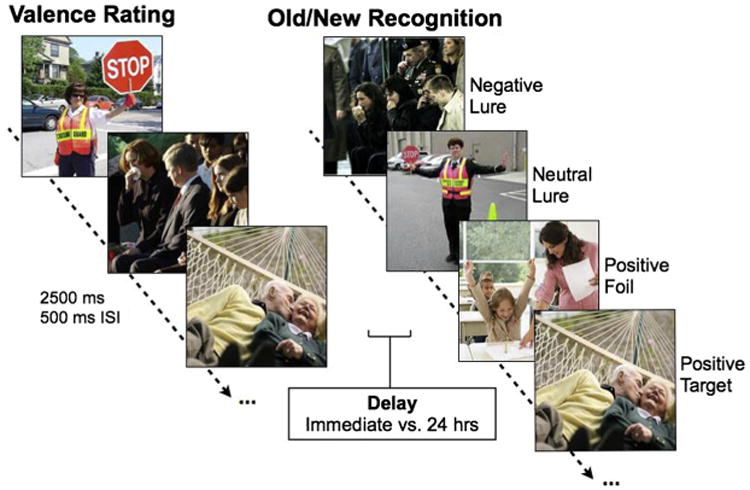
Emotional discrimination task design. During encoding, participants rated images according to their emotional valence from 1 (most negative) to 9 (most positive). Each image was presented for 2500 ms with a 500 ms inter-stimulus-interval (ISI). Either immediately after study or after a 24-h delay, participants underwent a surprise recognition test where they viewed negative, neutral, and positive targets, foils, and lures varying in similarity and were asked to indicate whether items were “old” or “new”.
