Figure 2. A diagram of representative components present in stress granules, grouped according to the known protein function.
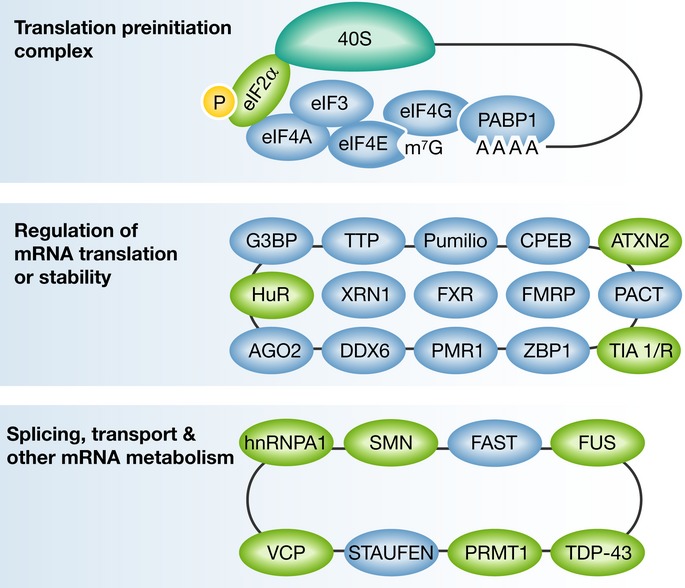
The translation preinitiation complex, including the small ribosomal subunit (40S; upper panel); RNA-binding proteins with role in regulation of mRNA translation or stability (middle panel); Splicing and other mRNA metabolism activities (lower panel). For comprehensive reviews see Anderson & Kedersha (2006, 2008), Buchan & Parker (2009) and references therein. Several of the presented RNA-binding proteins, depicted in green, were suggested to be involved in neurodegeneration. Incomplete list of references, linking particular stress granule components to motor neuron diseases include: eIF2α (Kim et al, 2014); HuR (Lu et al, 2009); TIA1 (Lu et al, 2009); SMN (Hua & Zhou, 2004); TDP-43 (Liu-Yesucevitz et al, 2010; McDonald et al, 2011); FUS (Bosco et al, 2010; Vance et al, 2013); hnRNPA1 (Kim et al, 2013); ATXN2 (Farg et al, 2013); VCP (Johnson et al, 2010; Buchan et al, 2013); PRMT1 (Tradewell et al, 2012; Yamaguchi & Kitajo, 2012).
