Table 1.
Steady-state parameters for amino acid activation by wild-type (WT) EcLeuRSa
| AA | AA structure | Km (AA) | kcat | kcat/Km | Discrimination factorb |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mM | s−1 | mM−1s−1 | |||
| WT LeuRS | |||||
| Leuc | 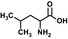 |
0.05 ± 0.01 | 66 ± 2 | 1,320 | |
| Nvac | 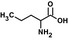 |
4.9 ± 0.4 | 56 ± 1 | 11.4 | 116 |
| Abad | 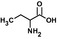 |
85 ± 9 | 20 ± 1 | 0.24 | 5,500 |
| Ilee,g | 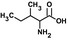 |
26 ± 7 | 1.1 ± 0.1 | 0.042 | 31,429 |
| M40G LeuRS | |||||
| Leuf | 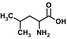 |
0.34 ± 0.03 | 6.9 ± 0.2 | 20 | |
| Nvaf | 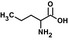 |
17 ± 3 | 4.2 ± 0.3 | 0.247 | 81 |
| Ilee, g | 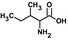 |
10 ± 2 | 1.14 ± 0.06 | 0.114 | 175 |
The values represent the best fit value ± s.e.m. of at least two independent experiments.
Measured by ATP-PPi exchange assay.
Discrimination factor is defined as (kcat/Km)cognate/(kcat/Km)non-cognate.
Parameters reported in (Cvetesic et al, 2012).
WT or M40G LeuRS were used at d10 nM, e150 nM, or f50 nM concentration, and Leu, Nva, and Ile concentrations were varied over the range 0.1–10 times the Km.
Isoleucine preparation used to determine activation parameters was purified as described in the Supplementary Materials and Methods.
