Figure 2. Design and function of mFGFR1-LOV domain chimeric receptors.
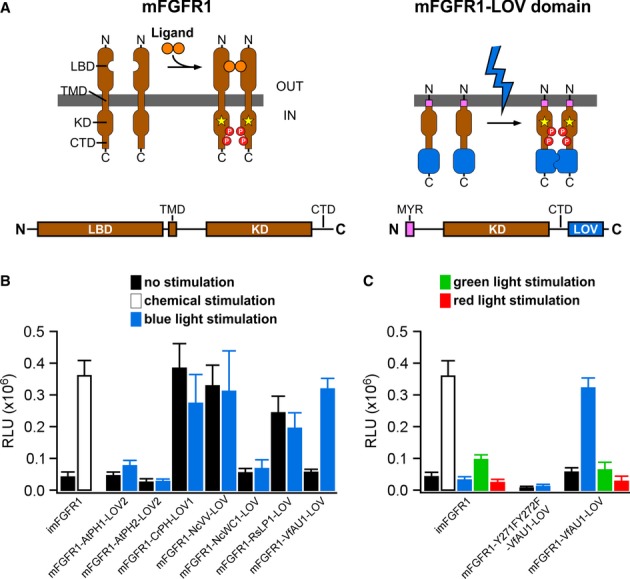
- Receptor tyrosine kinases such as mFGFR1 consist of the extracellular ligand-binding domain (LBD), single-span transmembrane domain (TMD) and intracellular domain (ICD) [kinase domain (KD) and a C-terminal tail domain (CTD)]. In mFGFR1-LOV domain chimeras, only the ICD is retained to render the protein insensitive to endogenous ligand. The ICD is attached to the membrane using a myristoylation domain (MYR) and LOV domains are incorporated at the ICD C-terminus.
- MAPK/ERK pathway activation in response to blue light for HEK293 cells that were transfected with chimeric proteins of mFGFR1-ICD and LOV domains. Activation is expressed as induction of a luciferase reporter gene. imFGFR1 is activated by the small molecule dimerizer AP20187.
- MAPK/ERK pathway activation in response to blue, green and red light for HEK293 cells that were transfected with imFGFR1, Opto-mFGFR1 (mFGFR1-VfAU1-LOV) or kinase dead Opto-mFGFR1 (Y271F, Y272F).
Data information: For (B) and (C): 24 h after transfection, cells were stimulated with light for 8 h followed by detection of luciferase. Light intensity was 1.7–2.5 μW/mm2. Mean values ± SEM for four to 16 independent experiments each performed in triplicates are shown.
