Figure 3. Analysis of Opto-mFGFR1 dimerization and sites required for MAPK/ERK pathway activation.
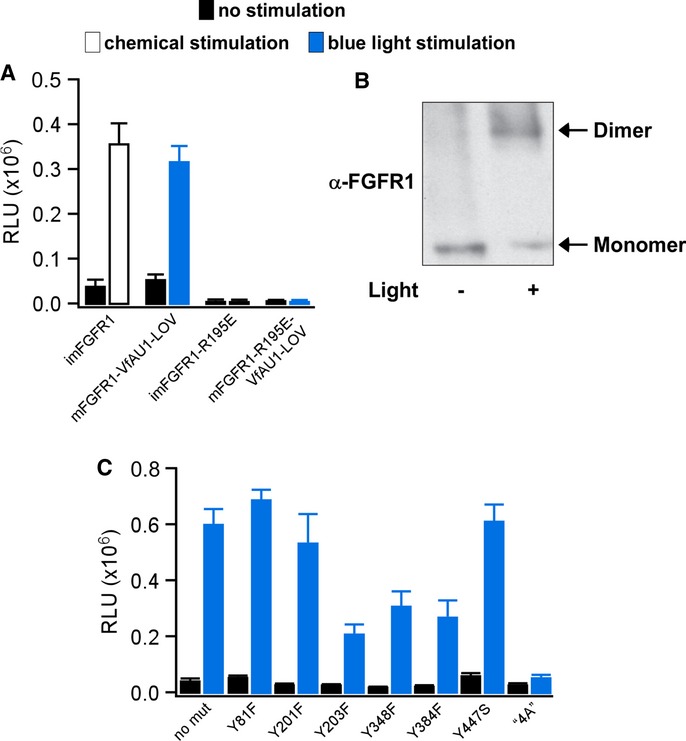
- MAPK/ERK pathway activation in response to blue light for HEK293 cells that were transfected with imFGFR1, Opto-mFGFR1 or genes with R195E substitution. This substitution prevents functional KD dimerization.
- Chemical cross-linking reveals light-induced dimerization of Opto-mFGFR1 in M38KOpto-mFGFR1 cells. Cells were stimulated with blue light for 15 min.
- Single-site or multi-site substitutions test phosphorylation site and coupling site requirements of Opto-mFGFR1. MAPK/ERK pathway activation in HEK293 cells that were transfected with Opto-mFGFR1 harbouring Tyr substitions at positions 81 (463), 201 (583), 203 (585), 348 (730), 384 (766) and 447 (3) or combined substitutions to Ala (‘4A’) at positions K37, P40, L41 and R43 (K419, P422, L423 and R425; numbering is relative to start methionine of Opto-mFGFR1; corresponding positions in mFGFR1 or VfAU1-LOV are given in parentheses). These residues were previously shown to be phosphorylated (Tyr) or required for association of FRS2 (LysProLeuArg).
Data information: For (A) and (C): 24 h after transfection, cells were stimulated with blue light for 8 h followed by detection of luciferase. Mean values ± SEM for two to 16 independent experiments each performed in triplicates are shown. For (A–C): Light intensity was ˜2.5 μW/mm2.
