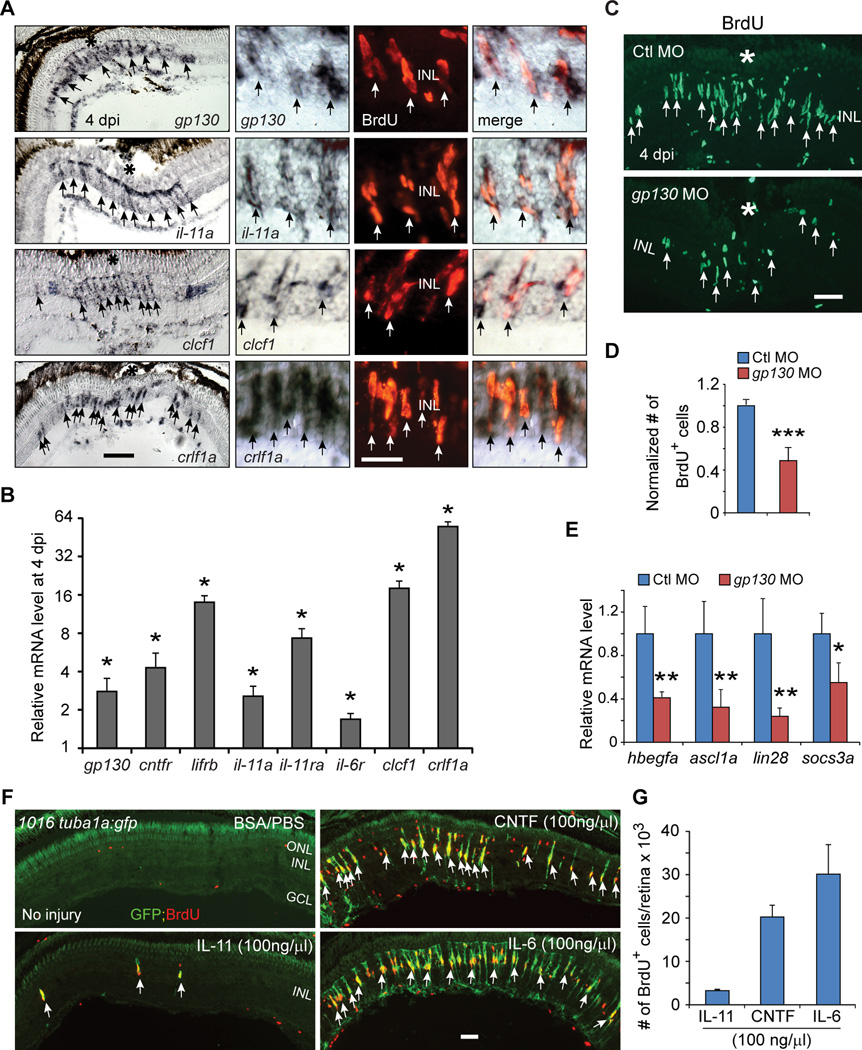
Figure 4. IL-6 family cytokines signaling through Gp130 are necessary and sufficient for retina regeneration.
(A) In situ hybridization and immunofluorescence shows that gp130, il-11a, crlf1a and clcf1 are expressed in BrdU+ MG-derived progenitors localized to the injury site. (B) qPCR quantifies il-6 family gene induction in MG-derived progenitors (FACS purified from 1016tuba1a:gfp fish retinas at 4 dpi) relative to MG from uninjured retina (FACS purified from uninjured gfap:gfp fish retinas); *P<0.05, n=3. (C, D) Gp130 knockdown inhibits the generation of BrdU+ MG-derived progenitors at 4 dpi. Control (Ctl) or gp130-targeting MOs were electroporated into the retina at the time of injury and fish received an i.p. injection of BrdU 3h before sacrifice on 4 dpi. ***P<0.001, n=4. (E) qPCR showing Gp130 knockdown inhibits injury-dependent induction of reprogramming genes at 2 dpi; *P<0.05, **P<0.01, n=4. (F) Intravitreal injection of recombinant mammalian IL-6-like cytokines into the uninjured eye of 1016tuba1a:gfp fish stimulates GFP expression and BrdU incorporation in MG throughout the retina’s inner nuclear layer. Intravitrial injection of PBS/BSA did not stimulate GFP expression or BrdU incorporation. The green fluorescence above the ONL in the top left-hand panel is autofluorescence unique to green channel (See Figure S7K). (G) Quantification BrdU+ cells following intravitreal injection of recombinant mammalian IL-6-like cytokines, n=3. Error bars, s.d. In (A, C), the asterisks mark the injury site (needle poke). Arrows point to MG-derived progenitors (A, C, F). Scale bars, 20 µm (A, C); 50 µm (F). ONL, outer nuclear layer; INL, inner nuclear layer; GCL, ganglion cell layer; dpi, days post injury. Primers are listed in Table S1. See also Figures S5 and S6.