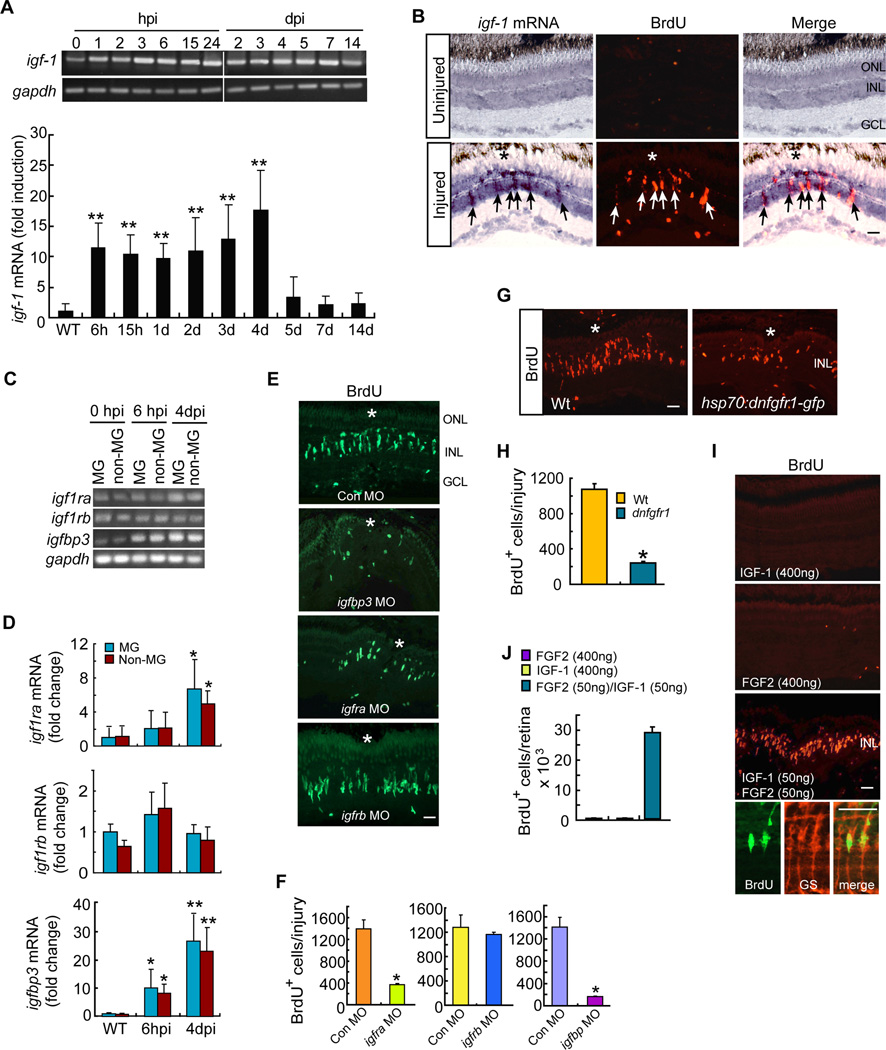
Figure 2. IGF-1 and FGF2 synergize with each other to stimulate MG proliferation in the uninjured retina.
(A) RT-PCR and qPCR analysis of injury-dependent induction of igf-1 mRNA. Error bars are SD; **P<0.001; n=6. (B) In situ hybridization shows injury-dependent induction of igf-1 RNA in BrdU+ progenitors (arrows) at 4 dpi. Scale bar is 50 µm. Asterisk marks the injury site. (C, D) RT-PCR (C) and qPCR (D) analysis of igf1ra, igf1rb and igfbp3 gene expression in FACS purified MG and non-MG at different times post retinal injury. Error bars (D) are SD; *P <0.05, **P<0.01; n=4. (E) BrdU immunofluorescence shows effect of morpholino (MO)-mediated knockdown of Igfbp3, Igfra or Igfbp on progenitor formation in the injured retina. Scale bar is 50 µm. Asterisk marks the injury site. (F) Quantification of BrdU+ cells in (E). Error bars are SD; *P <0.05; n=3. (G) BrdU immunofluorescence shows that conditional overexpression of dnFgfr1 in hsp70:dnfgfr1-egfp fish suppresses the generation of BrdU+ progenitors at 4 dpi. Asterisk marks the injury site. Scale bar is 50 µm. (H) Quantification of BrdU+ cells in (G). Error bars are SD; *P <0.05 n=3. (I) BrdU immunofluorescence shows IGF-1 and FGF2 synergize to stimulate MG proliferation in the uninjured retina. Scale bar is 50 µm. Bottom 3 panels show BrdU+ cells are also GS+ MG. (J) Quantification of BrdU+ cells in I. Error bars are SD; n=3. See also Figure S2.