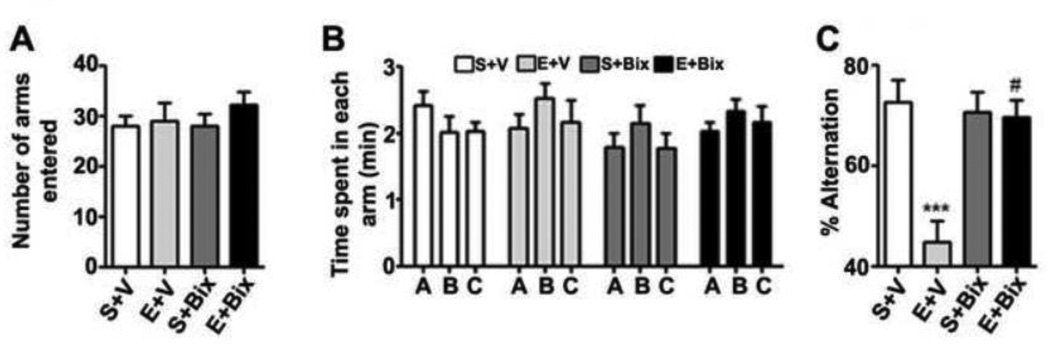
Fig. 4.
P7 ethanol treatment impairs and prior administration of G9a/GLP inhibitor prevents the spontaneous alternation performance deficit in adult mice. (A) Total number of arm entries reflecting exploratory activities of mice in the Y-maze does not differ between the four groups (p > 0.05). (B) The time spent in each arm was not different between four groups (p > 0.05). (C) The spontaneous alternation performance was reduced in by ethanol (E+V) and was rescued by Bix treatment (E+ Bix). Alternation performance was not affected by saline (S+V) and Bix (S+Bix) treatment. Each point is the mean ± SEM (n= 8 mice/group). (***p < 0.001 vs. S+V; #p < 0.001 vs. E+V) . One-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s post hoc test.