Fig. 3.
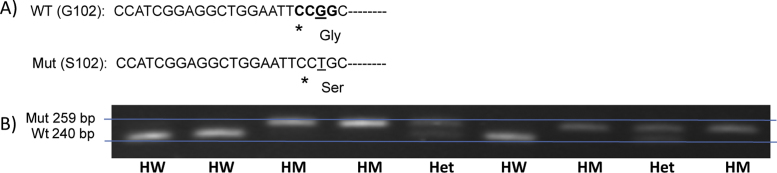
(A) Illustration of the principle underlying PCR-RFLP typing of the G102S SNP (rs2297950). Primers described by Bierbaum et al. (2006) result in amplification of a 259 bp gene fragment from genomic DNA located in Exon 4 and the following intron of the CHIT1 gene. The forward primer introduces a mutation (T → C, denoted by an asterisk) located just 2 nucleotides upstream of the position of the SNP, introducing an Hpa II restriction site (C′CGG, bold characters) for the wildtype G102 SNP (resulting in a 240 bp and a 19 bp fragment after restriction) but not the mutant S102 SNP (uncleaved 259 bp fragment). (B) Example of gel electrophoresis screening for CHIT1 G102S SNP following PCR and digestion with Hpa II. Higher bands indicate undigested allele containing S102 SNP, lower bands indicate large fragment of digested wild G102 allele. Single high band indicates homozygous mutant (HM), single lower band indicates homozygous wild type (HW) and presence of both bands indicates heterozygosity (Het).
