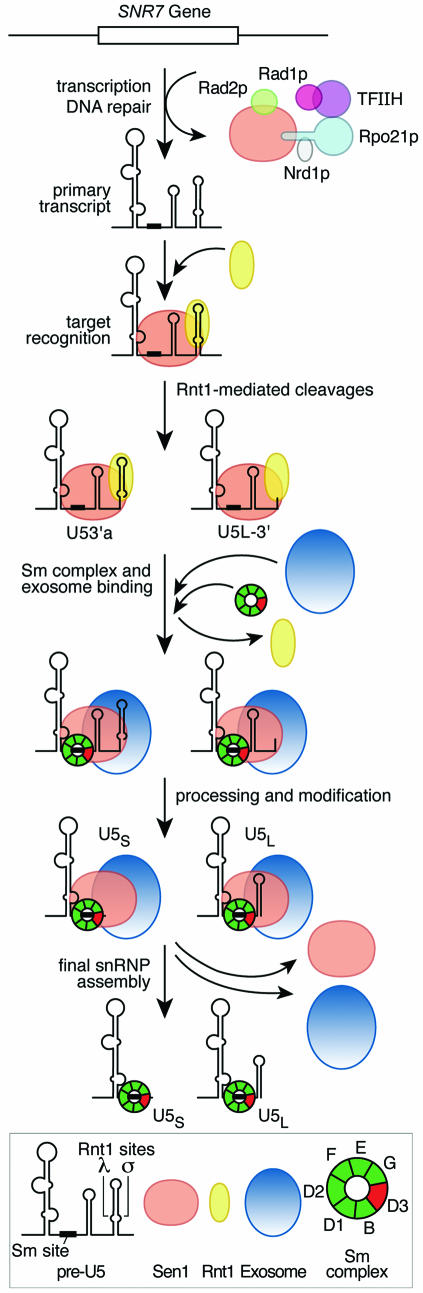
Figure 7.
Model for the role of Sen1p in the expression of the SNR7 gene coding for U5 RNA. The figure summarizes potential roles for Sen1p in transcription termination, transcription-coupled DNA repair, and RNA processing. Sen1p and Nrd1p have been implicated in transcription termination of non-coding RNAs (16,17). Rad1p and Rad2p are DNA endonucleases that cleave on the 5′ and 3′ sides of damaged DNA, and Rad1p is a subunit of transcription factor TFIIH (10,13,14). The primary events in the maturation of U5 RNA were described previously, including the involvement of Rnt1p (22,29,37), the exosomal and Rex nucleases (32,40), and the Sm complex (41,42). Data in this paper suggest a model in which a U5 post-transcriptional RNA complexes with Rnt1p and Sen1p; Rnt1p cleaves at the λ and σ cleavage sites and then dissociates; the seven subunit Sm complex associates with U5 RNA; Sen1p binds to one of the Sm subunits, Smd3p (12); and the exosome trims U5 RNAs yielding the two mature products, U5L and U5S. The Sm proteins and U5 RNA form the core U5 snRNP, but Sen1p dissociates and is not part of the final snRNP. Variations on the exact order of events are possible. It is not known whether the Sen1p that is bound to Rpo21p leaves with the polymerase after transcription is completed, in which case a second molecule of Sen1p must bind to the RNA, or whether the Sen1p molecule that functions in transcription remains bound to the RNA and functions with Rnt1p in subsequent processing events.