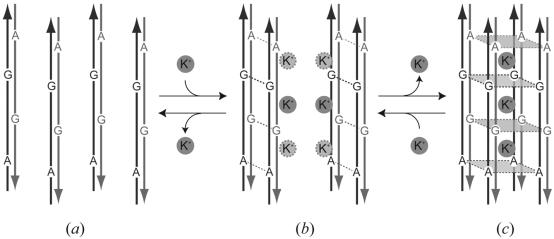
Figure 6.
Schematic diagram of the dynamic transition to form an octaplex. Arrows in gray and black represent 5′–3′ directions of DNA strands. Potassium cations are circled with gray. (a) Two octamers are aligned in an anti-parallel fashion and associate to form a base-intercalated duplex. (b) Two duplexes are associated to form a quadruplex through potassium-ion mediation. (c) Two quadruplexes assemble to make an octaplex by releasing some potassium cations.