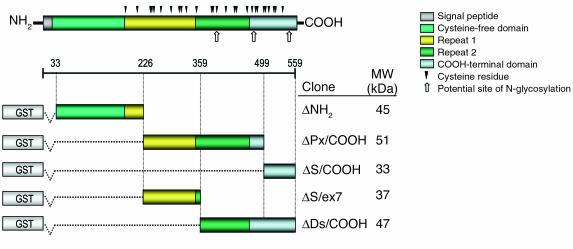
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of ECM1 protein and its five recombinant GST fusion fragments. The distinct molecular domains comprise a signal peptide, a cysteine-free NH2-terminal domain, two tandem repeat domains, and a COOH-terminal domain. The position of the single cysteine residues and potential N-glycosylation sites are indicated. The full-length 1.8-kb ECM1 cDNA was initially divided into three different fragments, ΔNH2 (33 to 226 amino acids), ΔPx/COOH (226 to 499 amino acids), and ΔS/COOH (499 to 559 amino acids), designed to span almost the entire ECM1. Two further fragments were then synthesized. The ΔS/ex7 fragment encodes part of the ΔPx/COOH domain (226 to 359 amino acids), and the ΔDs/COOH fragment encodes the distal part of the second tandem repeat domain and COOH-terminus (359 to 559 amino acids). All fragments were fused with GST-encoded cDNA at the NH2-terminus of the recombinant proteins. The amino acid residue numbers are shown as described elsewhere (13). The predicted molecular weights (kDa) of each recombinant fusion fragment are shown on the right.