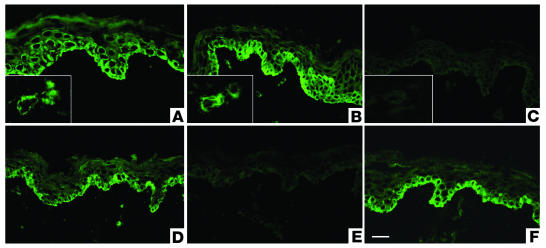
Figure 4.
Preabsorption assays for affinity-purified lichen sclerosus sera with recombinant proteins. (A) Immunostaining with anti-ECM1 rabbit polyclonal antibody on normal human skin displays intracellular labeling in the lower epidermis, particularly in basal and suprabasal cell layers. Inset shows labeling of dermal blood vessels. (B) Similar staining pattern was obtained using affinity-purified IgG fractions from ΔDs/COOH-positive lichen sclerosus sera. (C) Before immunostaining, the affinity-purified IgG fractions from ΔDs/COOH-positive sera were incubated with an excess of ΔDs/COOH recombinant. This results in a marked reduction in labeling intensity (c.f. Figure 4B). (D) Before immunostaining, the affinity-purified IgG fractions from a dual ΔNH2-positive and ΔDs/COOH-positive lichen sclerosus serum were incubated with an excess of either ΔNH2 or ΔDs/COOH recombinants. No alteration occurred in the original labeling intensity. (E) Before immunostaining, the affinity-purified IgG fractions from a dual ΔNH2-positive and ΔDs/COOH-positive sera were incubated with a mixture of both the ΔNH2 and ΔDs/COOH recombinants or with (F) control recombinant protein BP180 NC16A. Note the marked signal reduction in (E) but not in (F). Scale bar: 50 ∝m.