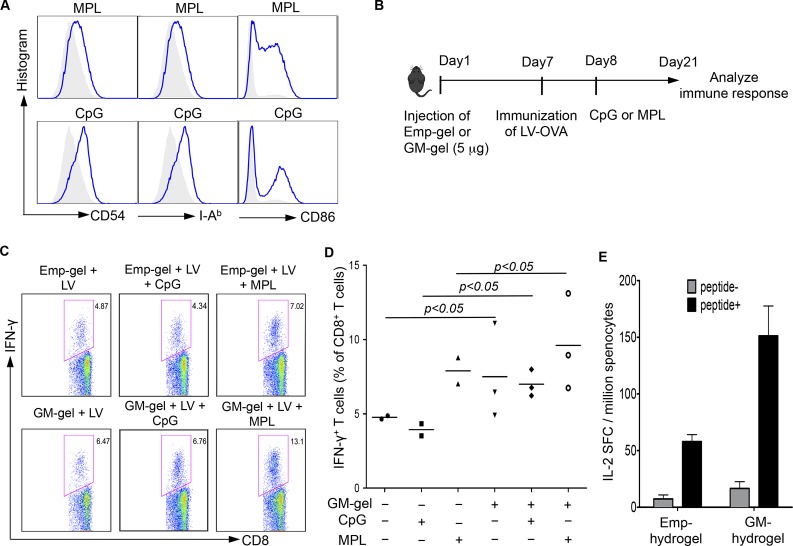
Figure 4.
GM-hydrogel allows for further modulation of resident DCs by adjuvants to enhance immune responses against specific antigen (OVA). (A) In vitro effects of adjuvants MPL and CpG on maturation of BMDCs. BMDCs were stimulated with 1 μg/mL MPL or 5 μM CpG overnight. The BMDCs were collected for staining of CD11c, I-Ab, CD54, and CD86. The result was analyzed by flow cytometry, and the expression of surface markers I-Ab, CD54, and CD86 was gated on CD11c+ DCs. (B) Schematic diagram showing the procedures. Seven days after injection of hydrogels with 5 μg of GM-CSF, mice were immunized with DC-LV-OVA. One day after immunization, the mice were injected with adjuvants (CpG or MPL). Two weeks after immunization, splenocytes were collected, and OVA-specific CD8+ T cells were analyzed by intracellular staining of IFN-γ expression. (C, D) GM-CSF hydrogels enable further enhancement of lentiviral vector-mediated immune responses with adjuvants. The FACS data are representative of four analyzed mice (C). Statistical data showing the percentage of IFN-γ+ cells within the CD8+ T cell population (D). (F) The effect of GM-CSF-loaded hydrogels on nonviral vector-mediated immune response. Seven days after injection of hydrogels with 5 μg of GM-CSF, mice were immunized with OVA protein and MPL. Seven days after immunization, splenocytes were pooled for an ELISPOT assay to analyze IL-2 secretion following stimulation with peptide for 18 h (n = 3).