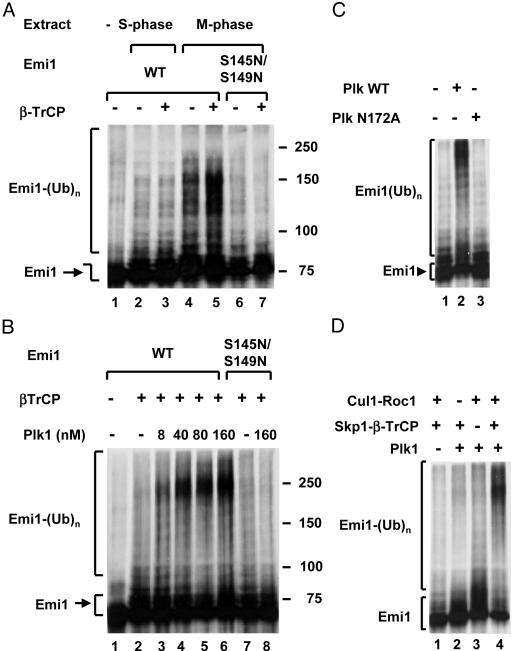
Fig. 1.
Plk1 is required for the ligation of Emi1 to ubiquitin (Ub) by SCFβ-TrCP. (A) The ubiquitylation of Emi1 is stimulated by β-TrCP in extracts from M-phase cells but not from S-phase cells. The ligation of ubiquitin to wild-type (lanes 1–5) or S145N/S149N mutant (lanes 6 and 7) is shown. Emi1 was determined as described in Methods in the presence of 30 μg of protein extract from HeLa cells arrested in the S phase (lanes 2 and 3) or M phase (lanes 4–7). Where indicated, 0.5 μlof β-TrCP-Skp1 was added. (B) Plk1 stimulates the ubiquitylation of Emi1 by purified SCFβ-TrCP. Ligation of wild-type or S145/S149N mutant Emi1 to ubiquitin was determined as described in Methods in the presence of the indicated concentrations of Plk1. (C) Requirement for enzymatic activity of Plk1. The ubiquitylation of Emi1 by SCFβ-TrCP was determined in the presence of a 160 nM wild-type or catalytically inactive (N172A) mutant of Plk1, as indicated. (D) Requirement for different components of SCFβ-TrCP. Where indicated, Cul1-Roc1 or β-TrCP-Skp1 was added at the amounts specified in Methods. Plk1 was added at 160 nM, and the ligation of Emi1 to ubiquitin was assayed.