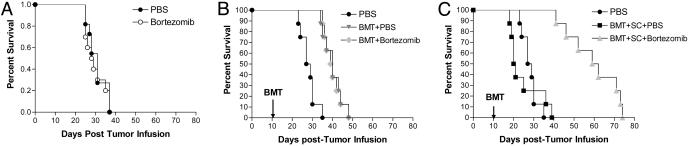
Fig. 5.
GVT activity is preserved with bortezomib administration after BMT. (A–C) B6 (H-2b) mice received 2 × 105 syngeneic C1498 cells on day 0. Effects of bortezomib administration on tumor survival were determined in various models. Mice received 15 μg per dose bortezomib or vehicle control (PBS) daily on days +11 and +13 after tumor injection. Results from one of three independent experiments are presented. Each experiment consists of 8–11 mice per treatment group. (A) No difference in survival was observed in nontransplanted mice. (B) Some groups were irradiated on day +10 after tumor cell injection, followed by injection of 15 million BALB/c (H-2d) bone marrow cells on day +11. Allogeneic BMT provided significant protection in tumor survival (P < 0.005) that was not changed by bortezomib administration. (C) In the same representative experiment as B, some groups additionally received 35 million BALB/c spleen cells. Mice that received vehicle control (PBS) injections succumbed to GVHD-associated morbidity. Mice that received bortezomib (▴) survived significantly longer than either untreated tumor-bearing mice (•; P < 0.0001) or mice that received a BMT with spleen cell and vehicle control treatment (▪; P < 0.0001).