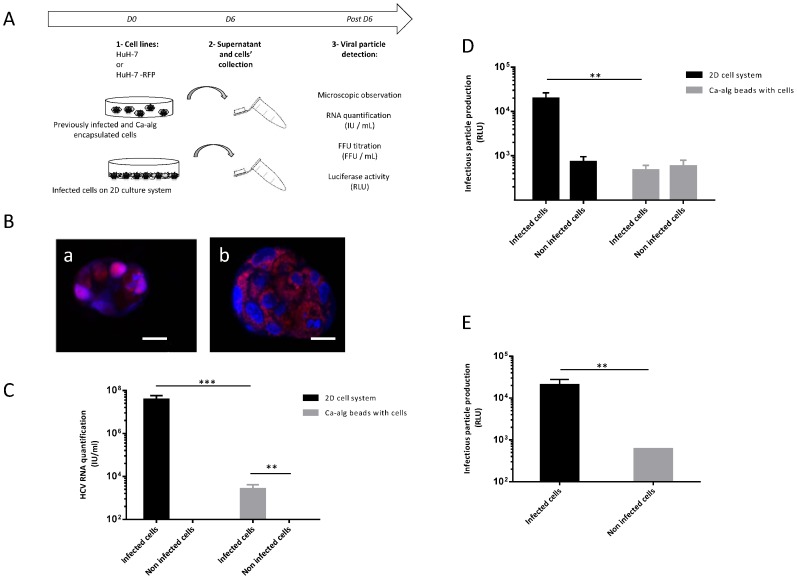
Figure 3. Absence of production of new HCVcc particles by previously infected and encapsulated cells.
(A) Encapsulated cell cultures were established using JFH1-RLuc virus-infected HuH-7 cells or non-infected cells within Ca-alg beads. Following the cell encapsulation stage, 400 µL of beads were transferred in tissue culture 6-well plates with 1 mL of complete DMEM medium added on 3D moving plates. (B) Foci of infected (a) or non-infected (b) HuH-7-RFP-NLS-IPS cells identified by translocation of the cleavage product RFP-NLS from cytoplasm to nucleus, were visualized at 6 days post-encapsulation by fluorescence microscope. Images are representative of three independent experiments. Nuclei were stained by DAPI. Scale bar 20 µm. The supernatants of the bead culture cells were collected at day 6 and incubated for 4 h with HuH-7 cell 2D cultures. (C) The amount of HCV RNA was quantified in the bead culture supernatants by RT-qPCR. Results are expressed as HCV RNA IU/mL and are reported as the mean ± S.D. of triplicate measurements. (D) Infectious particle production was assessed luciferase assay on infected cells at 72 h post-infection. Results are expressed as RLU and are reported as the means ± S.D. of three independent experiments. (E) Infectious particle production was also assessed by measuring Renilla luciferase activities after bead degelification to free previously infected cells and plating them. Results are expressed as relative light units (RLU) and are reported as the means ± S.D. of three independent experiments. **P<0.001, ***P<0.0001.