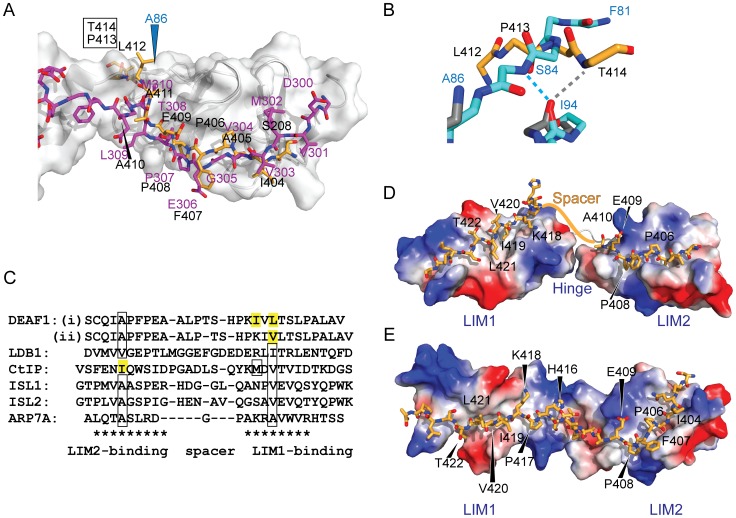
Figure 6. Tandem LIM LMO4-DEAF1 interactions.
(A) Comparison of the lowest energy member of the LMO4-DEAF1 complex ensemble (LMO4 in grey ribbon with blue labels and DEAF1 as orange sticks with black labels) and the LMO4-LDB1 complex (PDB accession code 1RUT, LMO4 with white surface and ribbon and LDB1 in magenta). Labels for residues in DEAF1 that clash with LMO4 in the LMO4-LDB1 structure are boxed. (B) Close up of the clashing region from the previous panel, using the same colouring, but with backbone residues from LMO4-DEAF1 (grey) and LMO4-LDB1 (cyan) shown as sticks and backbone-backbone hydrogen bonds with LMO4I94 shown in the same colours. Only the affected residues are shown for clarity. (C) Structure-based sequence alignment of characterised LIM-peptide complexes. Residues in bold appear to be important for binding based on mutational studies, boxed residues have been shown to be buried in the hydrophobic core between the two zinc-binding modules in the relevant LIM domain, and residues highlighted in yellow are predicted to be buried based on the alignment. LIM-binding motifs are indicated with asterisks. Residues in the spacer regions are generally not conserved but are shown for completeness. Two binding registers are proposed for the LIM1-binding residues in DEAF1. (D) Simple model for binding register (i). Structures for LMO4LIM1-CtIP and LMO4LIM2-DEAF1404–410 were aligned over the backbone atoms of the respective LIM domains in the LMO4-LDB1 structure (1RUT), and the residues in CtIP were altered to the correspond residues in DEAF1 using the mutagenesis module in PyMol. The linker between LIM1 and LIM2 from the LMO4-LDB1 structure is shown as a white cartoon. The approximate position of DEAF1411–415 is indicated with an orange line. (E) Homology model for binding mode (ii) using the structure of Lhx3–Isl1 as a template. In all cases where molecules are shown as sticks, nitrogen and oxygen atoms are shown in blue and red, respectively.