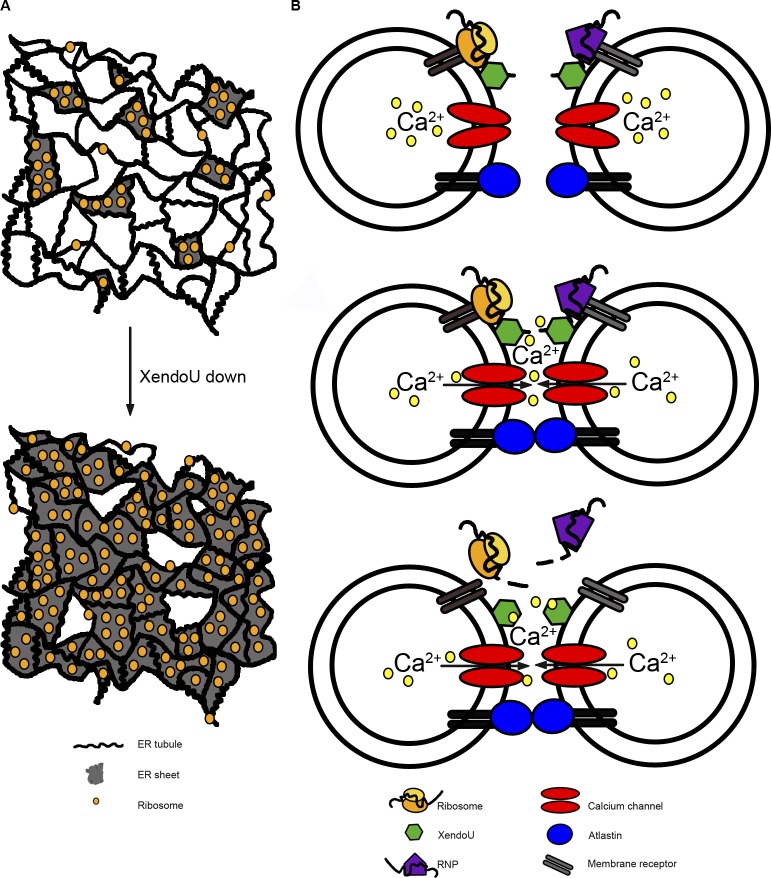
Figure 7.
Model of XendoU nuclease activity on membranes. (A) The ER network exists as a mixture of tubules and sheets. A decrease in XendoU results in the expansion of sheets. (B) Ribosomes, ribonucleoproteins (RNPs), XendoU, Atlastin, and (closed) calcium channels are localized to membrane vesicles containing Ca2+. Dimerization of Atlastin leads to eventual membrane fusion and calcium release through calcium channels on the membrane. XendoU binds calcium and mediates local RNA degradation (mRNAs, rRNAs, other RNAs), resulting in the release of ribosomes, RNPs, and RNA from the surface of membranes.