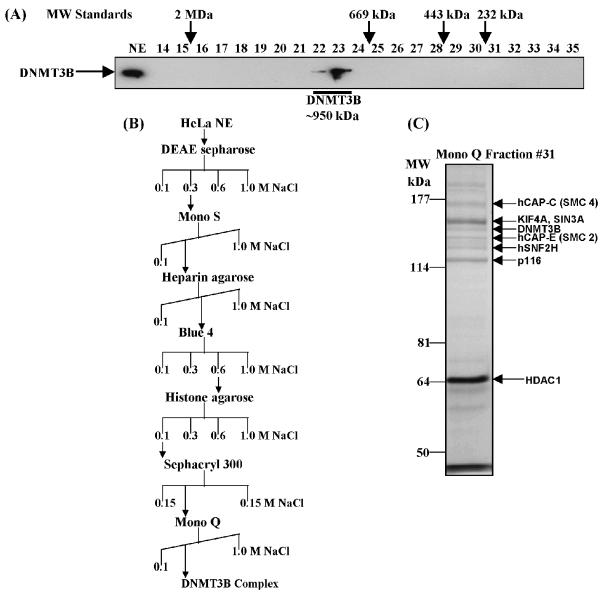
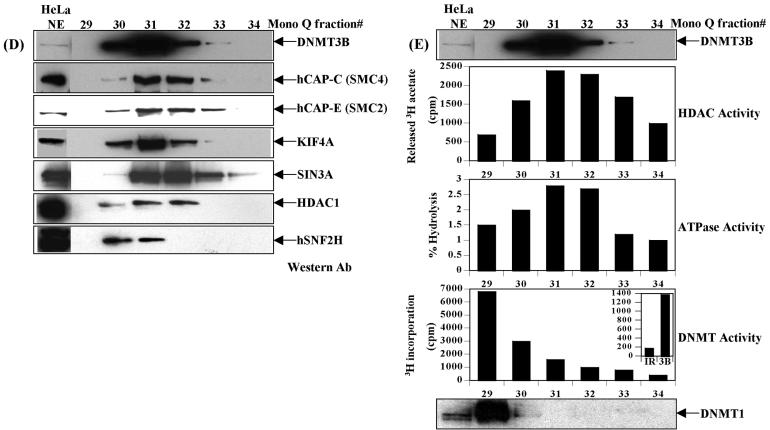
Figure 1.
Purification of a novel DNMT3B complex from HeLa cells. (A) Endogenous DNMT3B in HeLa nuclear extract (NE) migrates at a molecular weight of ∼950 kDa on a Superose 6 gel filtration column. The position of the size standards and column fraction numbers are shown along the top. Western blotting was performed with an epitope affinity-purified rabbit polyclonal anti-DNMT3B antibody. (B) Purification scheme for the DNMT3B complex. (C) Silver staining of the peak fraction of DNMT3B (detected by western blotting) from the final Mono Q purification step. Protein bands were excised from the gel and identified by mass spectrometry and/or western blotting, as described in Materials and methods. (D) Western blot analysis of the Mono Q column fractions across the peak of DNMT3B. Antibodies used in the western analysis are shown at the right of the figure. Fraction 31 was used for the mass spectrometry identification of DNMT3B co-purifying proteins. (E) Enzymatic activities co-purifying with the HeLa DNMT3B complex. Column fractions across the DNMT3B peak were screened for HDAC activity, ATPase activity (ATP hydrolysis stimulated by the addition of purified core histones) and DNA methyltransferase activity [with poly d(I-C) as the DNA substrate]. The inset shows the DNA methyltransferase activity from an immunoprecipitation with anti-DNMT3B antibody (‘3B’) demonstrating that the DNMT3B complex possesses DNA methyltransferase activity. ‘IR’ is an irrelevant antibody control (normal rabbit IgG). In the bottom panel, column fractions were probed for DNMT1 by western blotting.