Figure 2.
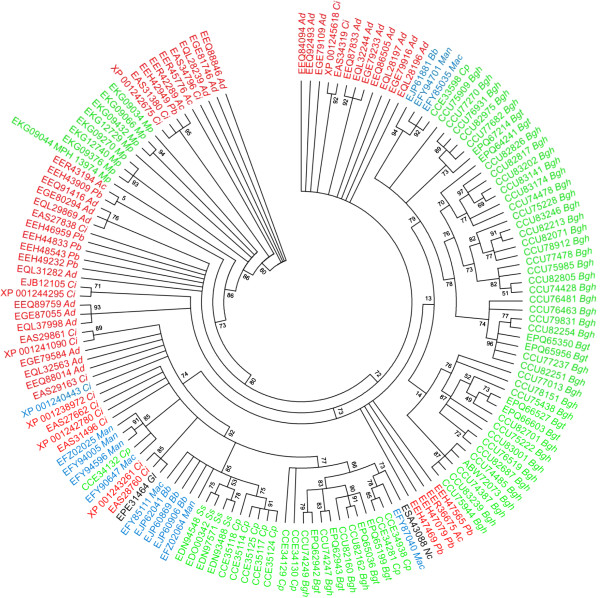
Cladogram of the fungus-specific kinase family. The tree integrates BLASTP results (E value <1e-20) using the Bgh protein CCU82254 as a query sequence. Phylogenetic analysis was performed with the tool Phylogeny.fr (http://phylogeny.lirmm.fr/phylo_cgi/index.cgi) with the following workflow: Protein sequences were aligned using MUSCLE3.7 with default settings. Poorly aligned positions and divergent regions were eliminated by Gblocks 0.91b with default settings. Presumably incomplete sequences (lacking an N-terminal methionine or < 250 amino acids) as well as sequences that were not properly aligned after curation were removed from the alignment. The phylogenetic tree was calculated by PhyML3.0 with computation of bootstrap values (100 replicates). MEGA6 was used to render the cladogram. Condensation of branches was performed with a cut off of for bootstrap values <2. Gene bank accessions and taxa are given in green (plant pathogenic fungi), red (human pathogenic fungi), blue (insect pathogenic fungi) and black (saprophytic fungi). Ac, Ajellomyces capsulatus; Ad, Ajellomyces dermatitidis; Bb, Beauveria bassiana; Bgh, Blumeria graminis f. sp. hordei; Bgt, Blumeria graminis f. sp. tritici; Ci, Coccidioides immitis; Cp, Claviceps purpurea; Fp, Fusarium pseudograminearum, Gl, Glarea lozoyensis; Mac, Metarhizium acridum; Man, Metarhizium anisopliae; Mp, Macrophomina phaseolina, Nc, Neurospora crassa; Pb, Paracoccidioides brasiliensis; Ss, Sclerotinia sclerotiorum.
