Figure 2.
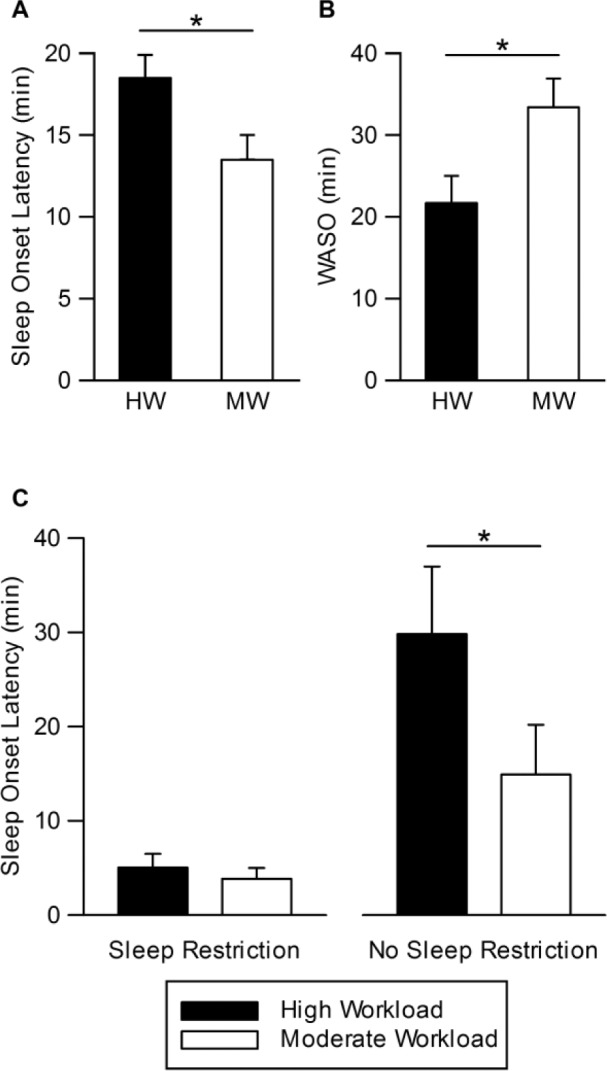
Effect of cognitive workload on sleep onset latency and wake after sleep onset. (A) Main effect of workload on sleep onset latency (SOL) and (B) wake after sleep onset (WASO), whereby HW produced longer SOL (d = 0.63) but shorter WASO (d = 0.64) than MW. Least Square Mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM), controlling for covariates (baseline night 3, age, and sex). (C) Mean (± SEM) sleep onset latency on the fifth protocol night. SOL on the fifth night in the high workload + no sleep restriction (HW + NSR) condition was longer than that in the moderate workload + no sleep restriction (MW + NSR) condition (right graph), indicating higher cognitive workload delayed sleep onset when there was no additional sleep pressure from sleep restriction. * P < 0.05. HW, high workload; MW, moderate workload.
