Figure 3. Mapping and modeling of apoptin motif responsible for its interaction with BCR-ABL1.
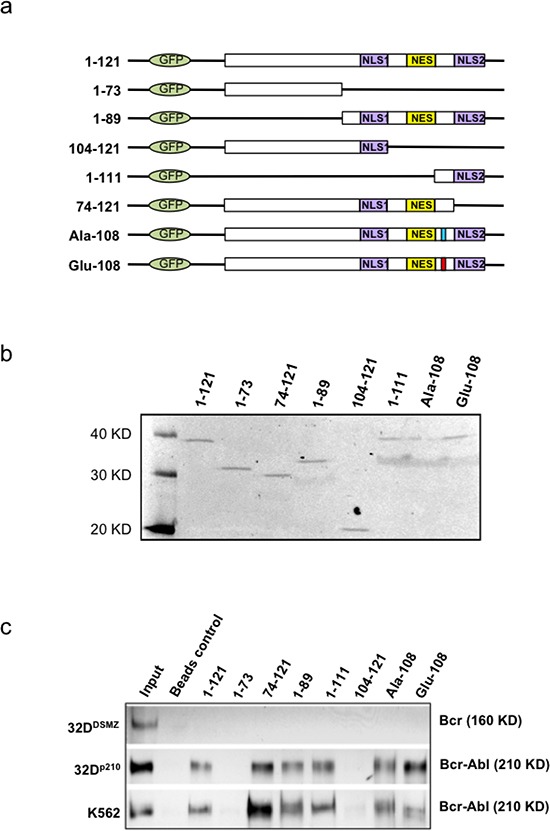
(a). Schematic representation of apoptin deletion mutants tagged with N-terminal GFP. (b). Immunoblot showing the expression of deletion mutants and wild type apoptin (1–121) transfected into PC-3 cells and immunoprecipitated with anti-GFP antibody 18 h post-transfection. (c). Apoptin CO-IP experiment from transfected 32DDMSZ, 32Dp210 and K562 cells with various mutant forms of apoptin; Bcr-Abl was identified in the immuno-precipitates of full-length apoptin and apoptin derivatives that harbored amino acids from 74-100 (includes the proline rich region, aa: 81-86) indicating a part of this region of apoptin is important for the interaction with Bcr-Ablp210.
