Figure 6. Anticancer action of apoptin targeting Abl/Bcr-Abl pathway.
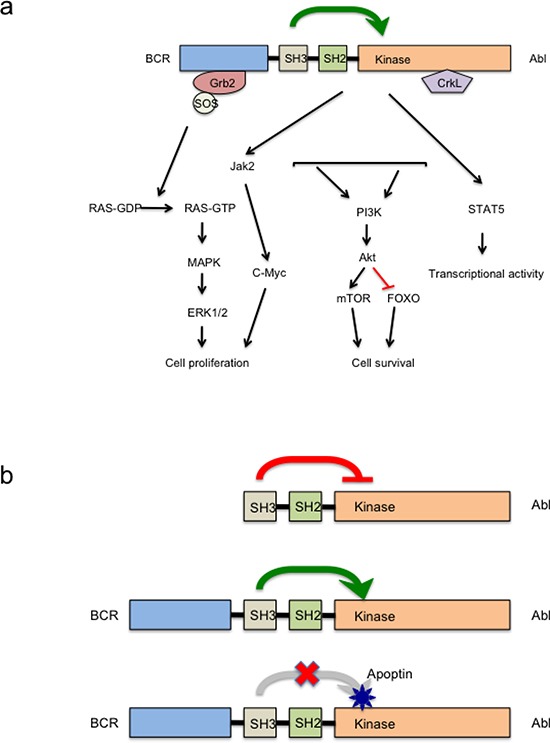
(a) Major signaling pathways activated in Bcr-Abl transformed cells. (b) Schematic diagram of apoptin induced Bcr-Abl kinase inhibition. UPPER PANEL- In normal c-Abl the SH3 domain acts as an endogenous inhibitor of its own kinase (SH1 domain) due to its interaction to a proline rich sequence of the same molecule. MIDDLE PANEL: In the fusion protein Bcr-Abl, the attachment of Bcr to the SH3 domain of Abl disrupts the attachment to this internal proline rich sequence and abrogates the kinase inhibition leading to autophosphorylation and transactivation of other oncogenic kinase pathways. LOWER PANEL: Strong interaction between the proline rich sequence of apoptin and the SH3 domain of oncoprotein Bcr-Abl leads of reinstitution of this inhibition on Bcr-Abl kinase.
