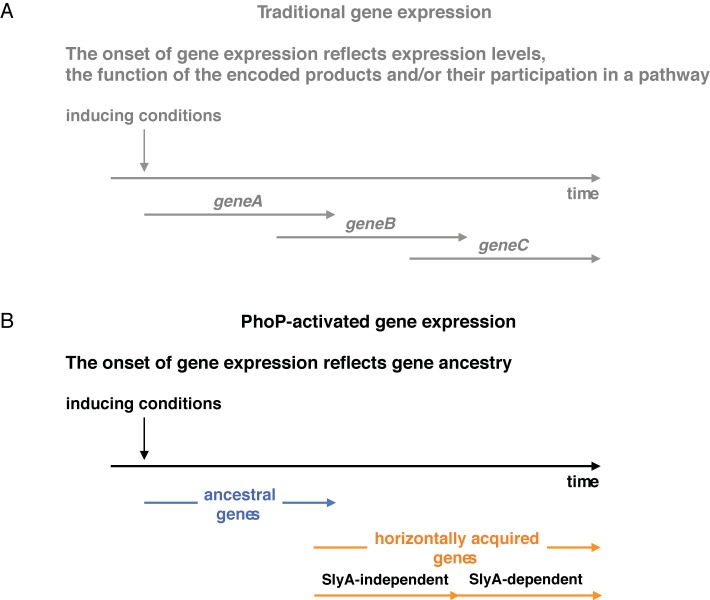
FIG 4 .
Gene ancestry determines the onset of expression of PhoP-activated genes. (A) The traditional view of gene expression timing. The onset of expression of genes controlled by a given regulatory protein reflects the levels at which the mRNA is produced (i.e., early genes are expressed at higher levels than late genes), the function of the encoded products, and/or their participation in a biochemical or morphological pathway. (B) PhoP-activated gene expression. The onset of expression of PhoP-activated genes reflects gene ancestry. Horizontally acquired genes are transcribed after ancestral genes due to the need to overcome H-NS-mediated silencing in the former. Among horizontally acquired genes, those that are dependent on the PhoP-activated SlyA protein are transcribed after those that are SlyA independent.