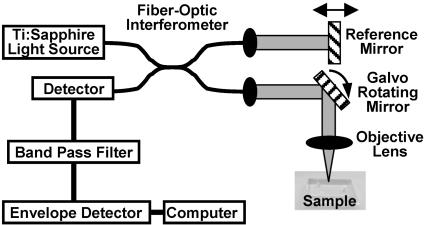
Fig. 1.
Schematic diagram of the OCT imaging system. Light from a low-coherence light source is split into two identical beams in a fiber-optic inter-ferometer and transmitted to a reference mirror and a sample. By measuring the interference between light backscattered from the sample and from the reference mirror, the distance and magnitude of optical scattering within the sample can be measured within micrometers. Scanning the light beam across the sample and recording the magnitude of the interference produces a complete cross-sectional image.