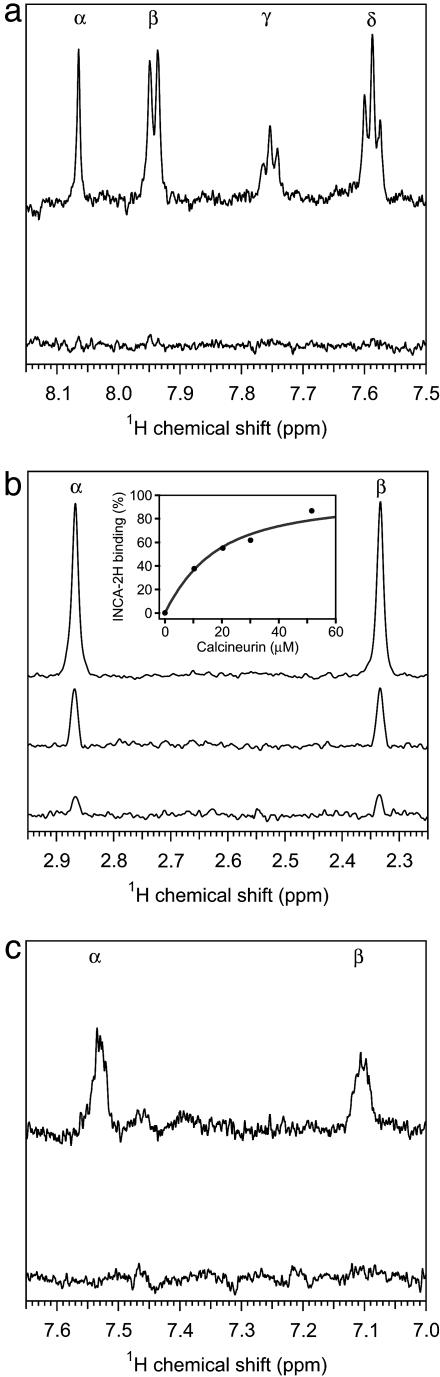
Fig. 3.
Evidence for direct interaction between INCA compounds and calcineurin. (a–c) T2-filtered 1H NMR spectra of 10 μM INCA compound in the presence of different concentrations of calcineurin. (a) INCA-1, resonances from protons at R1 (α) and at the ortho (β), para (γ), and meta (δ) positions of R2 in the presence of 0 μM (upper trace) or 20 μM (lower trace) calcineurin. (b) INCA-2H, methyl resonances from R3 (α) and R5 (β) in the presence of 0 μM (top trace), 30 μM (middle trace), or 52 μM (bottom trace) calcineurin. (Inset) Bound INCA-2H, determined from the intensity integral of the methyl resonances, is plotted as a function of total calcineurin concentration present in the sample. Modeling the situation as a two-state equilibrium gave the fitted curve with Kd 11.9 μM. (c) INCA-6, resonances from the benzene ring protons (α, β) in the presence of 0 μM (upper trace) or 20 μM (lower trace) calcineurin.