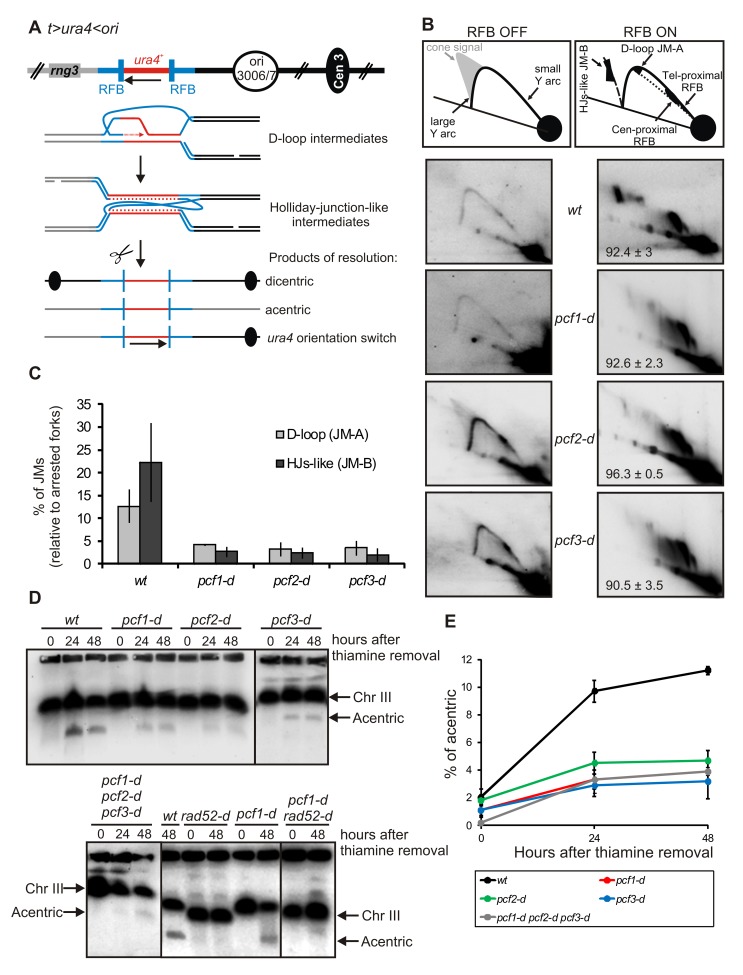
Figure 3. CAF-1 mediates template switch by stabilizing D-loop intermediates.
(A) Diagram of the t> ura4 <ori locus (see Figure 2 legend for details). Upon fork arrest at the RTS1-RFB, stalled nascent strands switch template and invade the opposite RTS1 sequence, leading to the formation of an early JM (D-loop, JM-A). The incoming of the opposite fork leads to a reciprocal template switch of stalled nascent strands leading to the formation of a late JM containing HJs (JM-B). The resolution of HJ-like structures leads to three distinct products: acentric or dicentric isochromosomes and the inversion of ura4 orientation (indicated by a black arrow). (B) Analysis of RIs by 2DGE in indicated strains and conditions; ON and OFF refers to the RTS1-RFB being active or not, respectively. Top panels are diagrams of RIs within the Ase1 restriction fragment analyzed by 2DGE in indicated conditions. Numbers ±SD, percentage of forks arrested at the RTS1-RFB. (C) Quantification of panel B. Values are the mean of three independent experiments ± standard error of the mean (SEM). Refer to Data S1, sheet 2. (D) Chromosomes from indicated strains and conditions were separated by PFGE and analyzed by Southern blotting using rng3 probe, located tel proximal from ura4. Cells were grown with (RFB OFF, time 0) or without thiamine (RFB ON) for 24 and 48 h. (E) Quantification of the amounts of acentric chromosomes seen in panel D. Values correspond to the mean of at least three independent experiments ±SEM. Refer to Data S1, sheet 3.