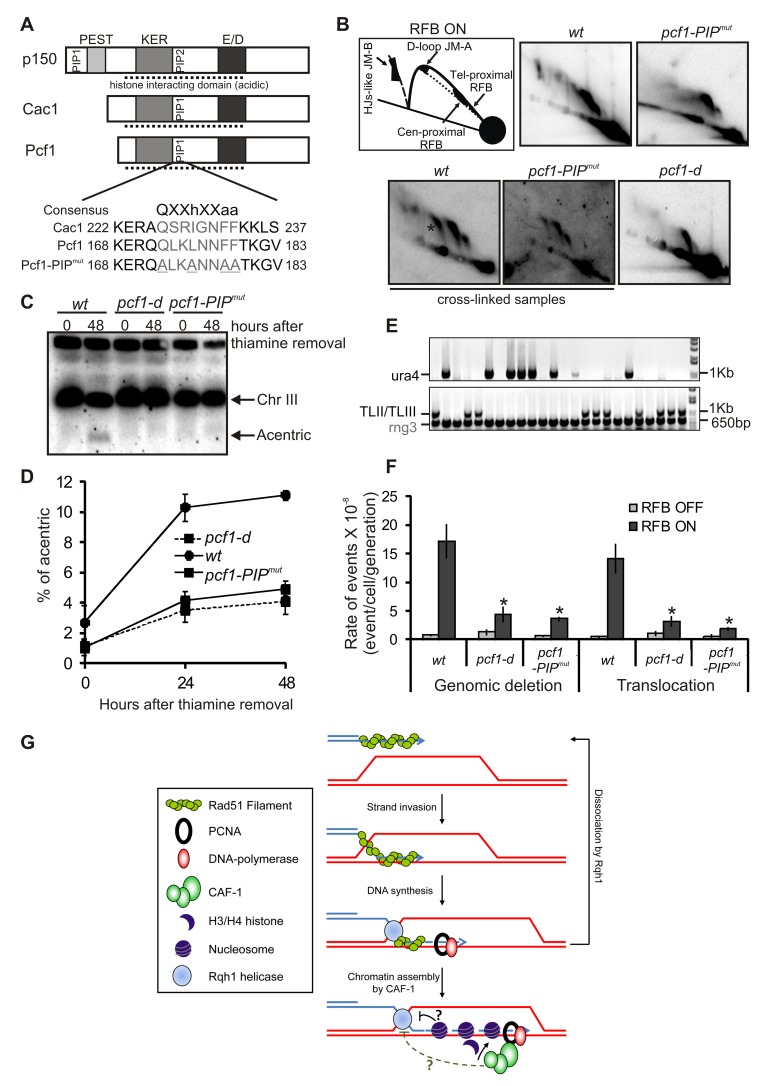
Figure 6. Preventing D-loop disassembly by CAF-1 requires its ability to interact with PCNA.
(A, Top panel) Alignment of the human (p150), S. cerevisiae (Cac1), and S. pombe (Pcf1) large subunit of CAF-1. Boxes indicate the PEST, KER, and E/D domains. The dashed line indicates the acidic region involved in histone binding. PIP1 and 2 indicate the PCNA interacting peptide. (Bottom panel) PIP1 sequence in Cac1 and Pcf1. Numbers refer to amino acids. Underlined amino acids indicate mutation introduced in the Pcf1-PIPmut protein. (B) Analysis of RIs by 2DGE in indicated strains and conditions; ON and OFF refers to the RTS1-RFB being active or not, respectively. Top panels are diagrams of RIs within the Ase1 restriction fragment analyzed by 2DGE in indicated conditions. Stars indicate additional signals resulting from partial digestion due to cross-linked DNA. (C) Chromosomes from indicated strains and conditions were separated by PFGE and analyzed by Southern blotting using rng3 probe, located tel proximal from ura4. Cells were grown with (RFB OFF) or without thiamine (RFB ON) for 48 h. (D) Quantification of the amounts of acentric chromosomes seen in panel C. Values correspond to the mean of at least three independent experiments ±SEM. Refer to Data S1, sheet 7. (E) Representative PCR amplification from 5-FOAR colonies from the indicated strain and condition. PCR products and their sizes are indicated on the figure. (F) Rate of genomic deletion and translocation for the strains indicated; ON and OFF refers to the RTS1-RFB being active or not, respectively. The percentage of deletion and translocation events, as determined by the PCR assay, was used to balance the rate of ura4 loss. The values reported are means of at least three independent median rates ±SD. Statistically significant fold differences in the rates of deletion or translocation events from the wt strain are indicated with an asterisk (p<0.01). Statistical significance was calculated using the nonparametric Mann–Whitney U test. Refer to Data S1, sheet 8. (G) Model of D-loop stabilization by CAF-1 during template switch. CAF-1 might prevent the disassembly of the D-loop by promoting histone deposition coupled to DNA synthesis. Nascent chromatin assembled on the D-loop then counteracts Rqh1 activity (black line). Alternatively, CAF-1 is targeting on the D-loop via its interaction with PCNA and counteracts the activity of Rqh1 directly or indirectly (dashed green line).