FIGURE 1:
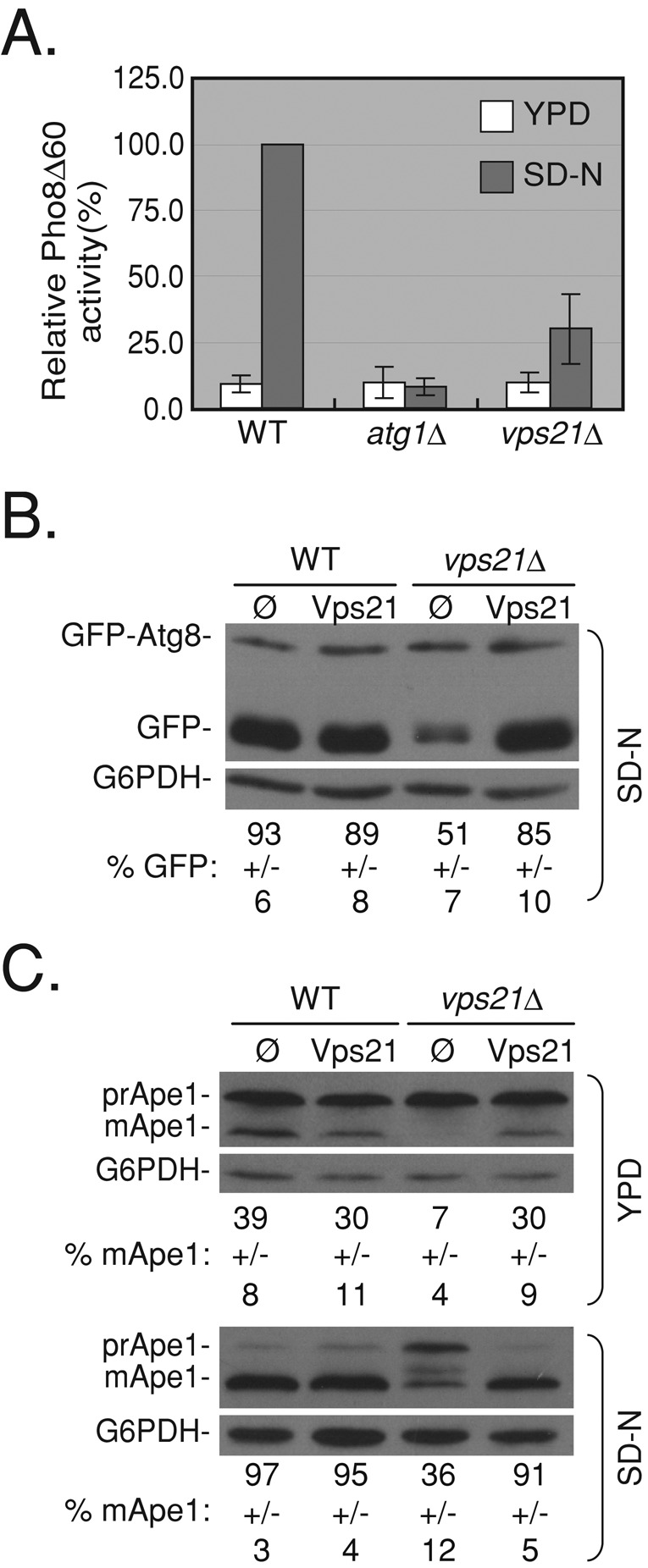
vps21∆ mutant cells are defective in selective and nonselective autophagy. (A) vps21∆ mutant cells are defective in nonselective autophagy measured by Pho8∆60 alkaline phosphatase (ALP) activity. ALP activity was determined in lysates of wild-type, atg1∆ (as a negative control), and vps21∆ mutant cells grown in rich medium (YPD, white bars) or starved for nitrogen (SD-N, gray bars). Vps21∆ mutant cells exhibit an autophagy defect under starvation when compared with wild-type cells (p < 0.001). (B) Vps21 suppresses the GFP-Atg8–processing defect of vps21∆ mutant cells under nitrogen starvation. GFP-Atg8 was integrated into the genome of wild-type and vps21∆ mutant cells. Cells transformed with a 2 μ plasmid for overexpression of Vps21 (empty plasmid [ø] as negative control) were grown in rich medium and shifted to SD‑N medium. GFP-Atg8 processing was determined in cell lysates using immunoblot analysis with anti-GFP antibodies (G6PDH serves as a loading control). In wild-type cells or in vps21∆ mutant cells expressing Vps21 from a plasmid, most of the GFP-Atg8 is processed to GFP. In vps21∆ mutant cells this processing is defective (p < 0.0001). (C) Vps21 suppresses the Ape1-processing defect of vps21∆ mutant cells grown in either rich or starvation medium. The experiment was done as described in B, except that Ape1 processing was determined using anti-Ape1 antibodies. In wild-type or vps21∆ mutant cells expressing Vps21 from a plasmid, premature Ape1 (prApe1) is processed to mature Ape1 (mApe1) in rich and starvation medium. In vps21∆ mutant cells, this processing is defective (p < 0.0008). Error bars and ± represent standard deviation (STD). Results represent at least three independent experiments.
