FIGURE 8:
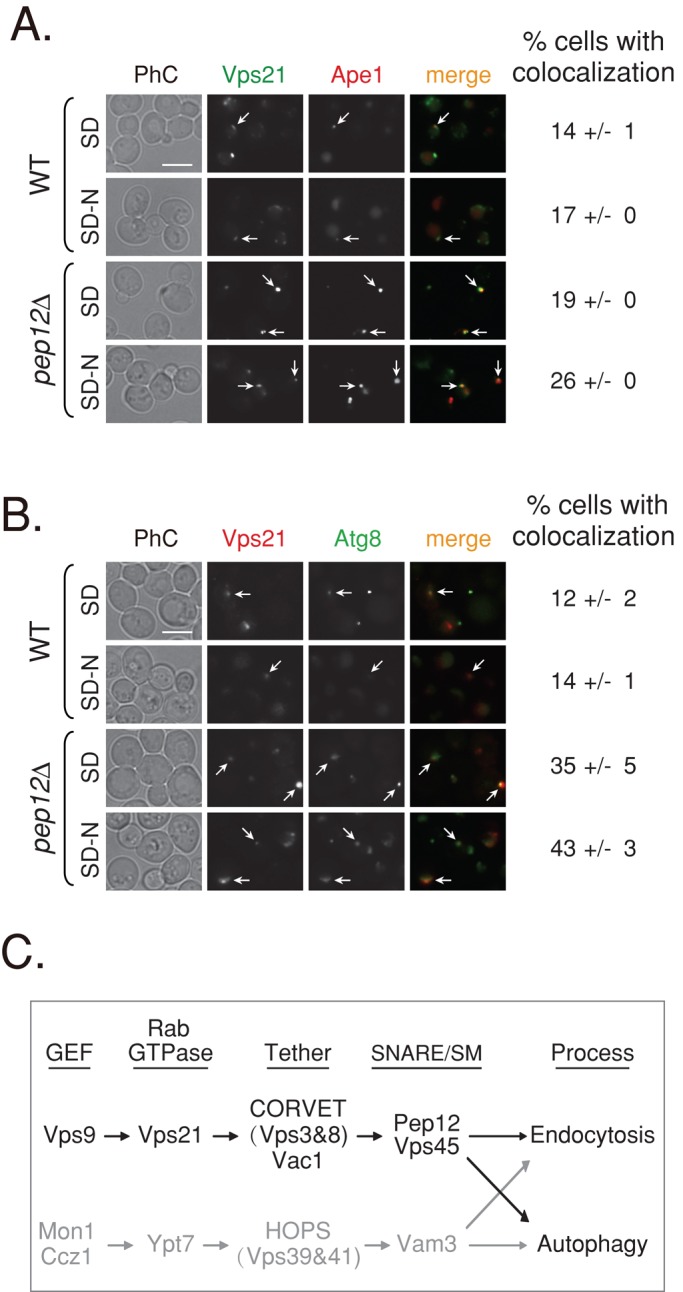
Vps21 colocalizes with autophagosomal markers. (A) Colocalization of GFP-Vps21 with RFP-Ape1 in wild-type and pep12∆ mutant cells. GFP-Vps21 and RFP-Ape1 were integrated into the genome of wild-type (top) and pep12∆ mutant (bottom) cells. Cells grown in SD or shifted to SD-N were visualized by live-cell fluorescence microscopy. Left to right, GFP-Vps21, RFP-Ape1, merge, and percentage of cells with colocalization. In wild-type cells, Ape1 is found inside the vacuole (Shintani et al., 2002) and localizes to a single dot of the AP. In pep12∆ mutant cells, Ape1 accumulates outside the vacuole in APs. Vps21 accumulates in multiple dots or a cluster per cell, and in 14–26% of the cells, one of the Vps21 dots colocalizes with Ape1. (B) Colocalization of RFP-Vps21 with GFP-Atg8 in wild-type and pep12∆ mutant cells. GFP-Atg8 was integrated into the genome of wild-type (top) and pep12∆ mutant (bottom) cells, and RFP-Vps21 was expressed from a plasmid (Markgraf et al., 2009). The experiment was performed as described in A. Left to right, RFP-Vps21, GFP-Atg8, merge, and percentage of cells with colocalization. In wild-type cells, Atg8 is found inside the vacuole and localizes to a single dot of the AP. In pep12∆ mutant cells, Atg8 accumulates outside the vacuole, in SD medium to a single dot, and in SD-N to a cluster (as in vps21∆ mutant cells). RFP-Vps21 localizes to multiple dots or a cluster, and one of them colocalizes with GFP-Atg8 in ∼14 and ∼43% of wild-type and pep12∆ mutant cells, respectively. Percentage of cells with colocalization of the Vps21 with the AP marker was determined in cells that contain both green and red puncta; >130 wild-type cells; >350 pep12∆ mutant cells. Arrows point to areas of colocalization of Vps21 with the AP marker; bar, 5 μm; ± represents SD. Results in A represent three independent experiments and in B four independent experiments. (C) Convergence of the endocytic and autophagic pathways. We propose that the two pathways leading to the lysosome converge through two Ypt/Rab modules: Vps21 (black) and Ypt7 (gray). Ypt7, its GEF, and effectors were previously shown to regulate both endocytosis and autophagy (Noda et al., 2009). A role for Vps21, its GEF, and effectors was established in endocytosis (Stack et al., 1995; Epp et al., 2011). Here we show that the endocytic Vps21 module also regulates autophagy. Factors that function downstream of Vps21 include a number of effectors, the tethering complex CORVET (Vps3 and Vps8), the adaptor/tether Vac1, and the SM protein Vps45, as well as the SNARE Pep12.
