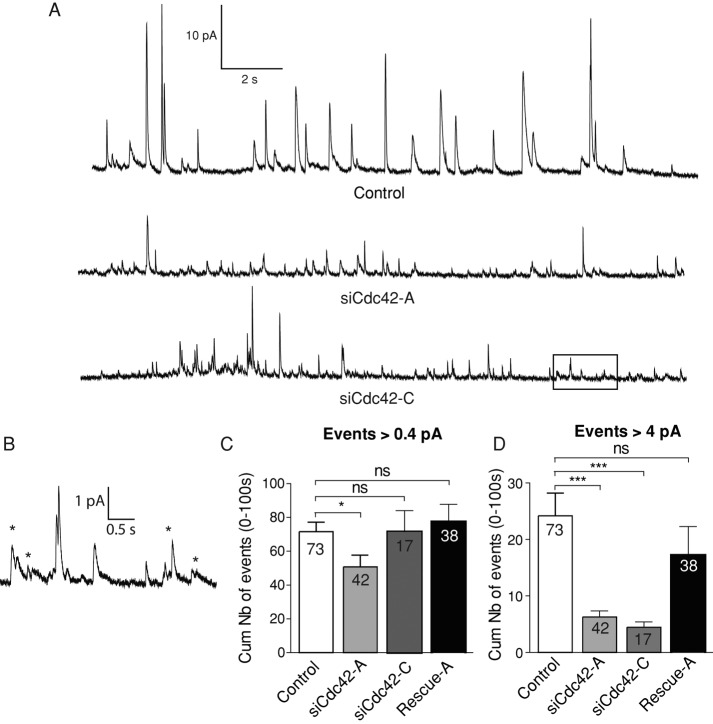
FIGURE 2:
Cdc42 knockdown reduces the occurrence of large spikes but not the overall probability of exocytosis. (A) Representative amperometric recordings of ionomycin-stimulated BON cells. Each spike reports an exocytotic event. (B) Enlarged view of a part (boxed area) of the bottom trace shown in A. Stars highlight events characterized by an irregular shape suggestive of fast fluctuations of the pore size. (C, D) Cumulative number of exocytotic events observed in stimulated BON cells treated with control siRNAs, siCdc42-A, or siCdc42-C, as indicated. Spikes were counted as an event when their height was >0.4 pA (C) or >4 pA (D). The significance of the differences was computed using a Kruskal–Wallis test followed by a Dunn's test for multiple comparisons. *p < 0.05; ***p < 0.001. Expressing a Cdc42 construct insensitive to siCdc42-A (rescue-A) reduced the effect of Cdc42 knockdown. Comparing siCdc42-A and rescue-A with a Mann–Whitney test yielded p = 0.0056 and 0.0207 in C and D, respectively. The number of cells is indicated in the bars.