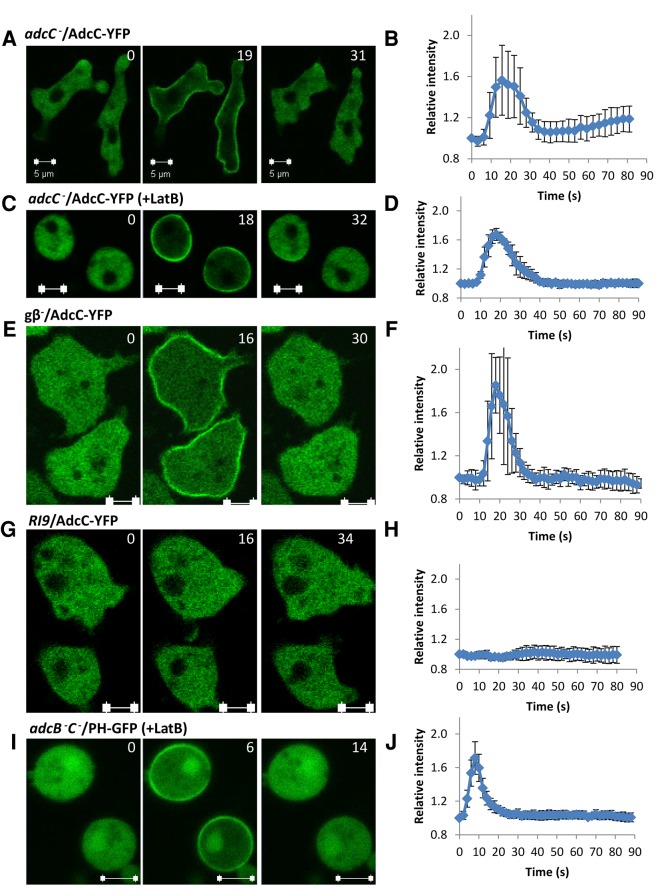
FIGURE 2:
AdcC transiently translocates from the cytosol to the cell membrane in an actin- and G protein–independent manner upon stimulation. (A) AdcC-YFP transiently associates with plasma membrane upon cAMP stimulation. adcC− cells expressing AdcC-YFP were stimulated with 10 μM cAMP. (B) Kinetics of the time course. Means (n = 7) and SDs are shown. (C, D) cAMP-induced AdcC membrane translocation does not depend on the actin cytoskeleton. adcC− cells expressing AdcC-YFP were treated with latrunculin B to depolarize the actin cytoskeleton and stimulated with cAMP. Means (n = 6) and SDs are shown. (E, F) cAMP-induced AdcC membrane translocation does not require Gβ. Translocation of AdcC-YFP in gβ− cells was monitored by time-lapse confocal microscopy after cAMP stimulation. Means (n = 6) and SDs are shown. (G, H) cAMP-induced AdcC membrane translocation requires cAR1 signaling. Temporal changes in the levels of AdcC-YFP at the plasma membrane are shown as a time course for RI9 (car1-/car3-) cells expressing AdcC -YFP. Means (n = 6) and SDs are shown. (I, J) cAMP-induced PHCRAC-GFP translocation appears normal in arrestin-null cells. adcB−C− cells expressing PHCRAC-GFP were treated with latrunculin B to depolarize the actin cytoskeleton and stimulated with cAMP. The levels of PHCRAC-GFP at the plasma membrane are shown as a time course. Means (n = 6) and SDs are shown. Scale bar, 5 μm. In A and B, images were captured at 3.1-s intervals, and in B–J, images were captured at 2-s intervals; selected time points are shown.