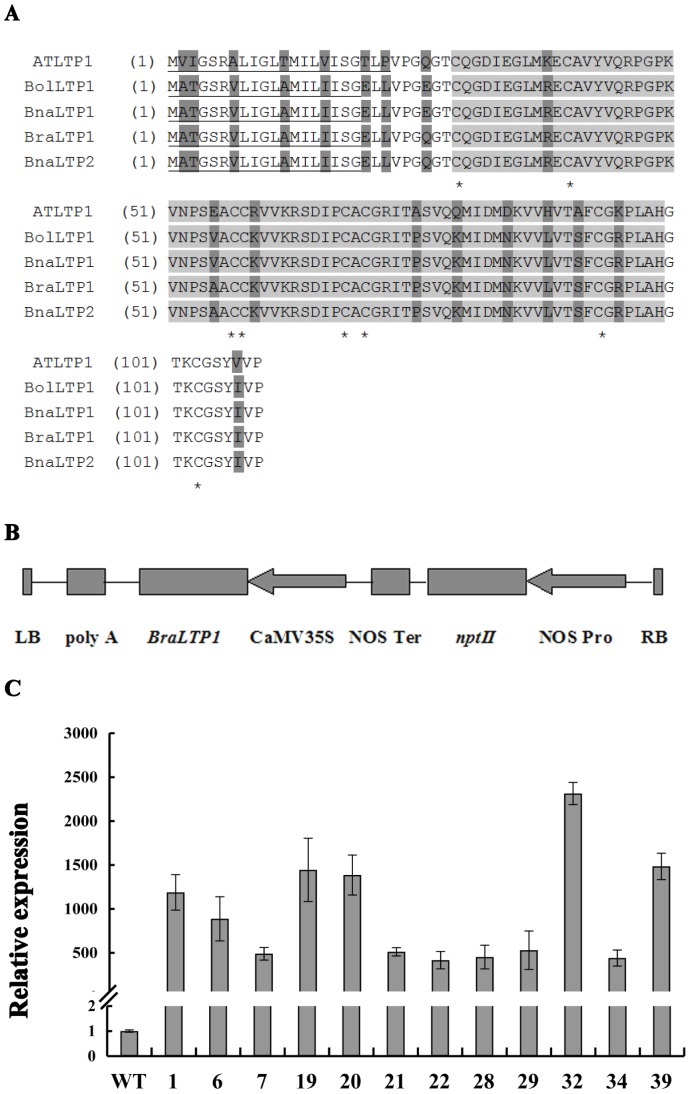
Figure 1. Basic protein characteristics of BraLTP1 and vector construction.
(A) Analysis of the deduced amino acid sequences of BraLTP1 with its homologous sequences in other cruciferae; variable sites (dark grey)the nsLTP-like conserved 8 CM domain (light gray) with conserved cysteine residues (asterisks) and putative extracellular secretory signals (underlined). Sequences are from Arabidopsis thaliana AtLTP1 (AT4g30880), B. rapa BraLTP1 (Bra011229) [32], B. oleracea BolLTP1 (Bol018048) [60], B. napus BnaLTP1 (AY208878), and B. napus BnaLTP2 (KM062522). (B) T-DNA region of the BnaLTP1 overexpression construct containing BnaLTP1 driven by the CaMV 35S promoter. LB = Left border, RB = Right border, poly A = poly A terminator, nptII = kanamycin resistance, NOS Ter = nopaline synthase terminator, NOS Pro = nopaline synthase promoter. (C) Analysis of BraLTP1 mRNA levels in 10-week-old wild type (WT) and T0 35S::BraLTP1 transgenic plants by qRTPCR. Transgenic plants include BraLTP1-1, -6, -7, -19, -20, -21, -22, -28, -29, -32, -34 and -39. Standard errors were derived from three repeated experiment for the expression levels of each plants.