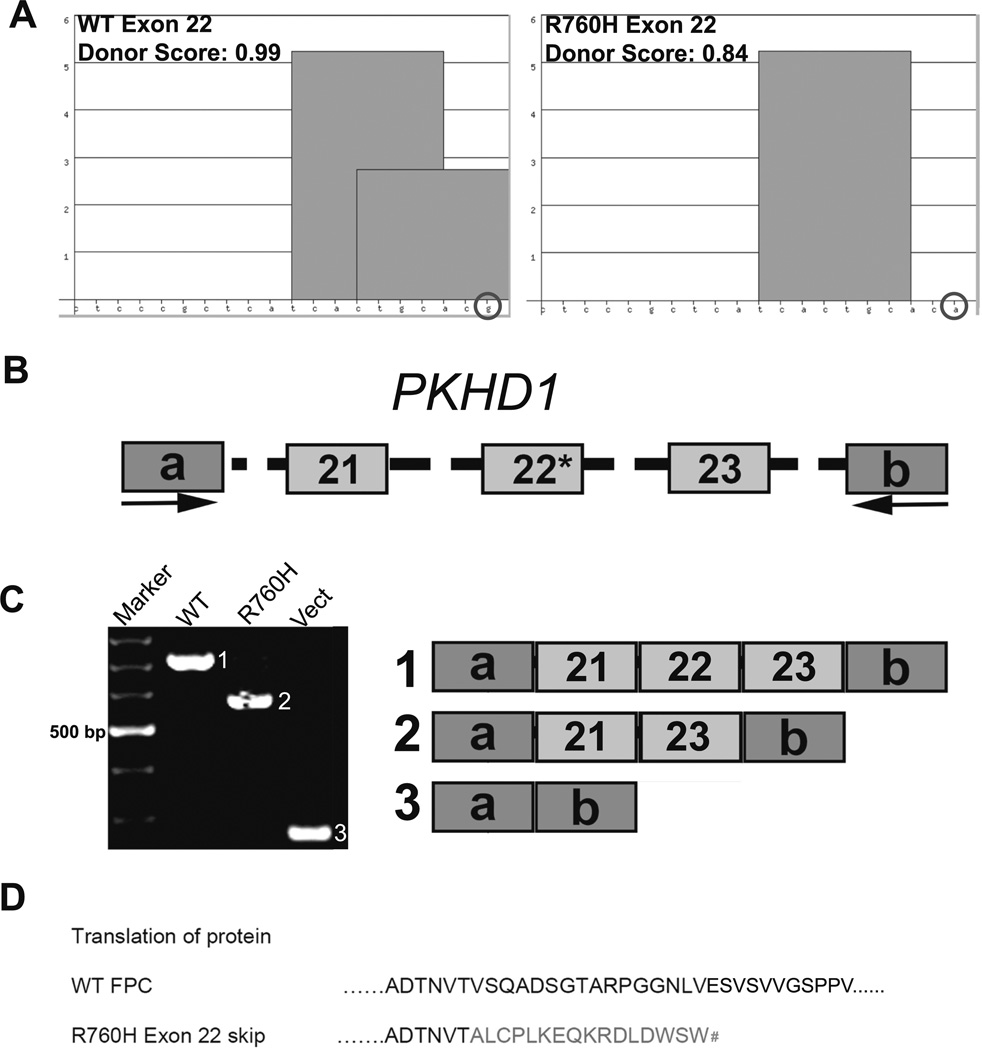
Fig. 8.
PKHD1 missense variant R760H is inefficiently spliced. a ESE Finder 3 analyses identified an SRSF5 motif in the 3′ end of WT PKHD1 exon 22, while analysis of the R760H variant revealed loss of the motif. The nucleotides are indicated along the X-axis, whereas the Y-axis represents the strength of the SRSF5 motifs; SSPNN donor scores are listed. b WT or R760H minigene constructs containing human PKHD1 exons 21, 22, and 23 with 200 bp of flanking intronic sequences were cloned into pSPL3 vector (mutation indicated by R760H). c Representative RT-PCR results are shown. The WT minigene yielded only the canonical 706 bp PKHD1 product containing exons 21, 22, and 23 (WT lane, product 1). The mutant construct (asterisk) generated a product of 567 bp due to skipping of exon 22 (Mut lane, product 2). The empty vector was used as a control (Vect lane, product 3). d Translation of the wild-type and mutant peptide sequences is shown. With the skipping of exon 22, the predicted exon 21–23 junction results in a frame shift that leads to a premature stop codon (number sign). a, b Vector specific exons. All amplified products were sequence confirmed