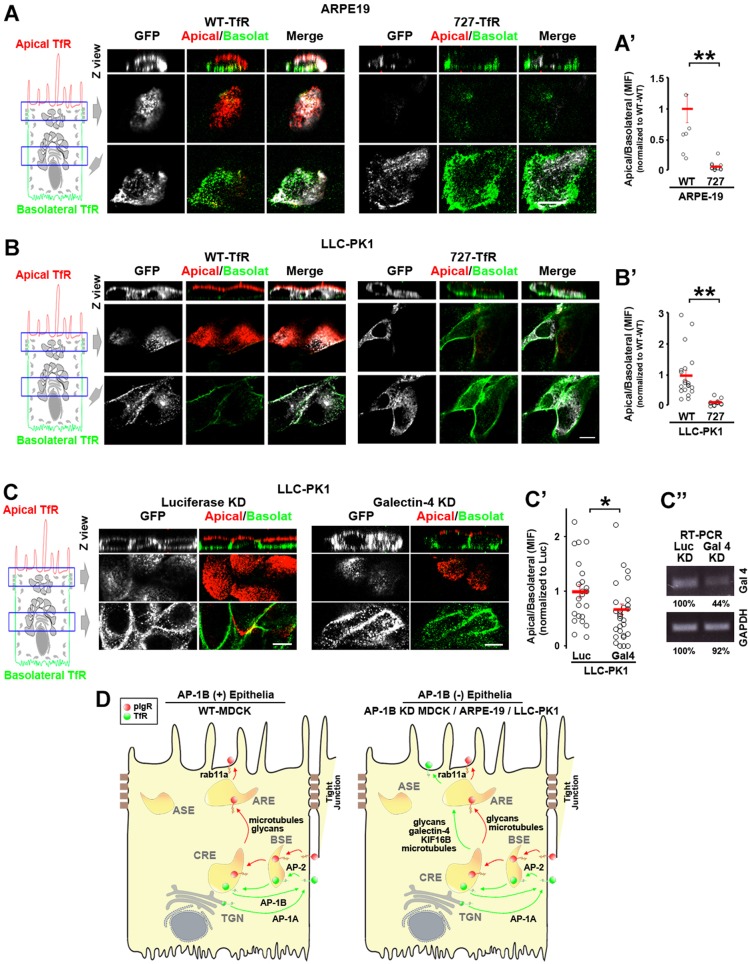
Fig. 7.
The N727-glycan signal/galectin-4 sorting machinery operates in constitutively AP-1B-deficient epithelial cells. (A) Polarized ARPE-19 (A) and LLC-PK1 cells were transiently transfected with either WT- or N727A-TfR–GFP. Cells were immunostained for surface TfR–GFP (without permeabilizing the cells) using anti-GFP primary antibody and Alexa-Fluor-568-conjugated anti-rabbit-IgG (red) and Alexa-Fluor-647-conjugated anti-rabbit-IgG (green) secondary antibodies in the apical and basolateral chambers, respectively. (A′,B′) Cells from experiments represented in A and B were quantified for the apical:basolateral ratio using the fluorescence signal of each plasma membrane domain. (C) LLC-PK1 cells were knocked down for luciferase (Luc) or galectin-4 and polarized on transwell filters. Apical and basolateral TfR was immunostained in the same manner as above. (C′) Cells from experiments represented in C were quantified for the apical:basolateral ratio using the fluorescence signal of each plasma membrane domain. (D) Model. Polarized WT MDCK cells display TfR basolateral recycling mediated by the clathrin adaptor AP-1B and apical transcytosis of pIgR. In contrast AP-1B-deficient epithelial cells, such as AP-1B KD MDCK, ARPE-19 and LLC-PK1, transcytose a substantial fraction of TfR to the apical plasma membrane via AREs, mediated by the N727-linked glycan signal, galectin-4, Rab11a, microtubules and the microtubule motor KIF16B. Circles correspond to individual cells obtained from different experiments and red lines indicate the mean±s.e.m. *P<0.05, **P<0.001. Scale bars: 10 µm.