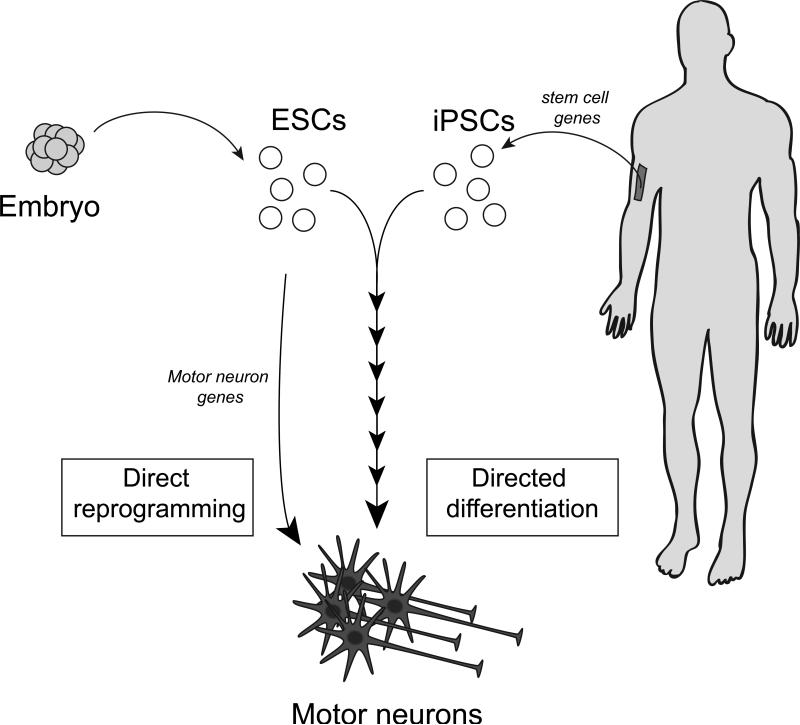
Figure 3. Making motor neurons from stem cells.
Embryonic stem cell lines (ESCs) are generated from early human embryos, whereas differentiated skin cells can be turned into induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) by upregulating specific stem cell genes. Both ESCs and iPSCs can be directed to differentiate into motor neurons through a multi-step process by culturing them for weeks in the presence of factors that mimic normal neuronal development (“directed differentiation”). A more rapid process (days) is the “direct reprogramming” of ESCs (or fibroblasts, not shown) into motor neurons directly by forced expression of motor neuron genes.