Figure 2.
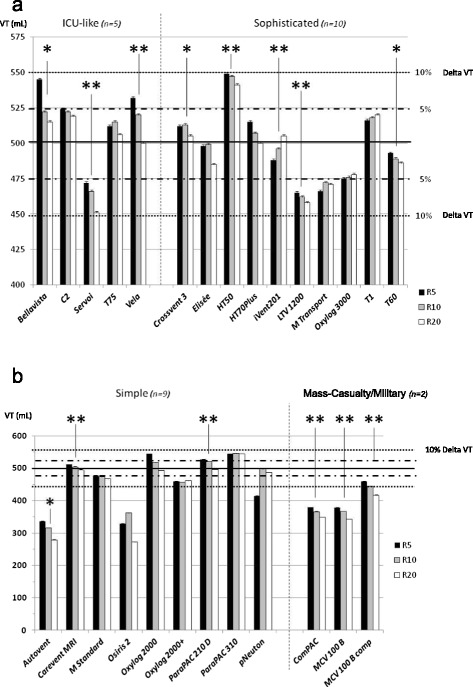
Individual tidal volume delivery according to respiratory mechanics changes. Values are provided as mean ± STD; VT, tidal volume; R, different values of resistance were applied (5, 10 and 20 cm H2O/L/s) in combination with different compliance (30, 70, 120 cm H2O/L); dotted line represents the 10% accuracy range and the hashed line the 5% accuracy range; a P-value equal to or below 0.05 was considered significant; *P <0.05; **P <0.005. (a) All ventilators in the ICU-like and sophisticated emergency and transport ventilator (ETV) categories were within the 10% accuracy range for VT, and most of them within the 5% accuracy range; 8 of 15 ETV depicted an impact of respiratory mechanics changes over VT accuracy; (b) 6 of 11 ventilators in the simple and mass-casualty/military categories developed VT below the 10% accuracy range, and 6 of them depicted an impact of respiratory mechanics changes over VT accuracy. However, for most of them, the increase in resistance, combined with high compliance, was responsible of a pressure-release safety valve opening (major overdistension related to a low expiratory flow), which meant that they were not able to deliver ventilation.
