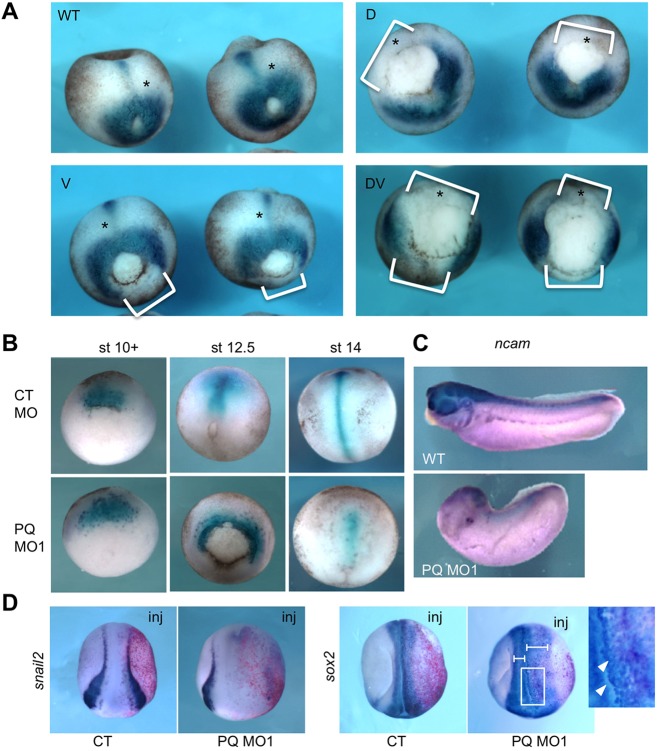
Fig. 3.
The effects of PQBP1 knockdown on embryonic mesoderm and neurectoderm. (A) Expression of the pan-mesodermal marker brachyury (bra) in late gastrula (stage 12.5) embryos injected with 20 ng pqbp1 MO1 into dorsal (D), ventral (V) or both (DV) blastomeres at the four-cell stage. Note lack of bra expression wherever the pqbp1 MO was injected (white brackets). (B) Expression of the dorsal (axial) mesoderm marker chordin in embryos injected dorsally with 20 ng of either control MO (CT MO) or pqbp1 MO1 (PQ MO1) at the four-cell stage. (C) Expression of neural marker ncam in uninjected (WT) or pqbp1 MO1-injected embryos targeted dorsally as in B. Lateral views with anterior to left. (D) Expression of the neural crest marker snail2 (slug) and the neural marker sox2 in neurula embryos (stage 19) injected in a single two-cell stage blastomere with 20 ng pqbp1 MO1 or control MO (CT) along with β-galactosidase lineage tracer (red). Dorsal views with anterior down. Perturbed neural folding is shown by differences between width of left and right neural folds (brackets). Loosely adherent sox2-positive cells, marked by arrowheads in the magnified view of the boxed area. WT, wild-type control embryos.