Fig. 6.
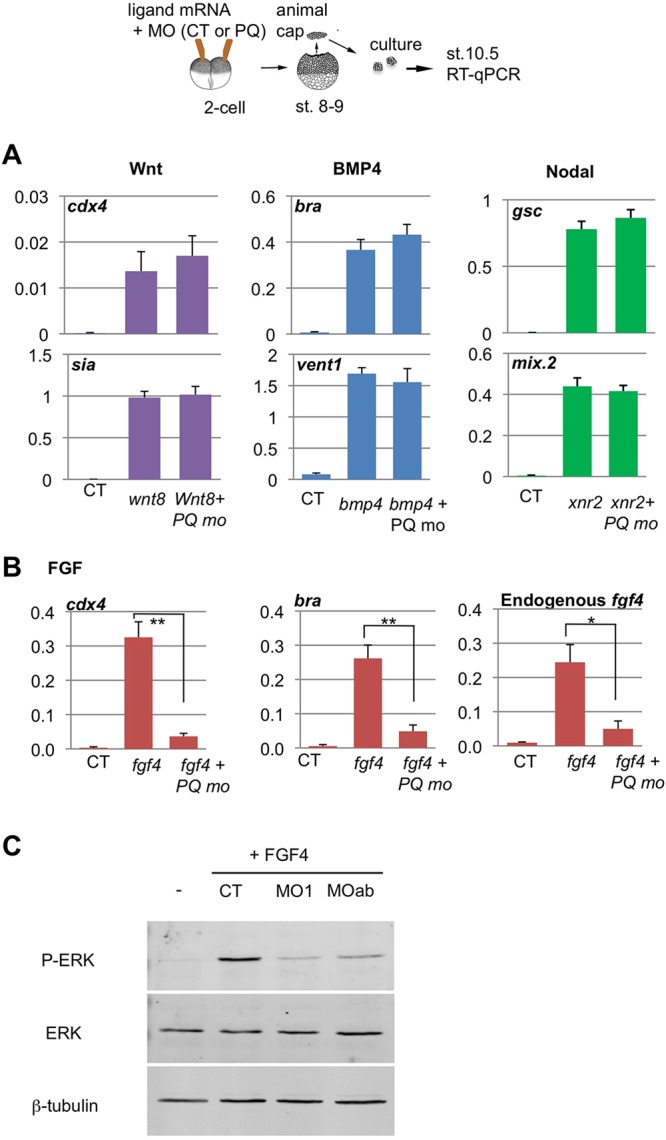
Effects of PQBP1 knockdown on animal cap response to growth factors. (A,B) Two-cell embryos were injected into the animal pole with growth factor mRNAs and MOs, animal caps were cut at mid-blastula and harvested at the equivalent of early gastrula stage, followed by qPCR, as depicted (top). Results were analyzed and plotted as per Fig. 5. (A) Marker gene induction by Wnt8 (50 pg), BMP4 (500 pg) and Nodal2 (Xnr2; 100 pg) was not affected by PQBP1 knockdown (50 ng MO). There was no statistically significant difference between CT and PQBP1 MO-injected caps treated with each ligand (Student's t-test, n=3). (B) Marker gene induction by FGF4 was significantly reduced by PQBP1 knockdown (*P<0.05 or **P<0.01; Student's t-test, triplicate biological replicates). Animal caps were injected with fgf4 mRNA (1 pg) and either control MO (50 ng), pqbp1 MO1 (50 ng) or MOa+MOb (25 ng each). (C) Phosphorylation of MAPK (Erk) was induced in fgf4-injected animal caps, but blocked by co-injection of pqbp1 MO, either MO1 or MOa+MOb. The levels of β-tubulin and total MAPK protein did not change among these samples.
